Interrupted-time-series analysis of the immediate impact of COVID-19 mitigation measures on preterm birth in China
- PMID: 36057724
- PMCID: PMC9440464
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-32814-y
Interrupted-time-series analysis of the immediate impact of COVID-19 mitigation measures on preterm birth in China
Abstract
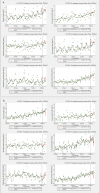
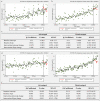
Preliminary evidence from China and other countries has suggested that coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) mitigation measures have caused a decline in preterm births, but evidence is conflicting. Utilising a national representative data of 11,714,947 pregnant women in China, we explored the immediate changes in preterm birth rates during the COVID-19 mitigation period using an interrupted-time-series analysis. We defined the period prior to February 1, 2020 as the baseline, followed by the COVID-19 mitigation stage. In the first month of the COVID-19 mitigation, a significant absolute decrease in preterm birth rates of 0.68% (95%CI:-1.10% to -0.26%) in singleton, and of 2.80% (95%CI:-4.51% to -1.09%) in multiple births was noted. This immediate decline in Wuhan was greater than that at the national level among singleton births [-2.21% (95%CI:-4.09% to -0.34% vs. -0.68%)]. Here we report an immediate impact of COVID-19 mitigation measures on preterm birth in China.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- WHO: recommended definitions, terminology, and format for statistical tables related to the perinatal period and use of a new certificate for cause of perinatal deaths. Modifications recommended by FIGO as amended October 14, 1976. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 56, 247–253 (1977). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

