Clinical significance of gastroesophageal reflux disease with minimal change: a multicenter prospective observational study
- PMID: 36057730
- PMCID: PMC9440892
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-19408-w
Clinical significance of gastroesophageal reflux disease with minimal change: a multicenter prospective observational study
Abstract
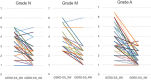
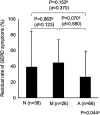
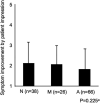
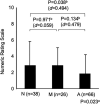
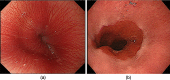
Non-erosive reflux disease (NERD) is classified into grade N (no minimal change) and grade M (minimal change) based on the Los Angeles classification. However, few reports have described the clinical characteristics of grade M. This study was performed to clarify the clinical characteristics of grade M. Among 290 consecutive patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), 45 patients with grade M, 62 patients with grade N, and 94 patients with grade A were compared with respect to clinical differences. The degree of symptom improvement after 4 weeks of proton pump inhibitor administration was also prospectively compared among the three groups. Grades N and M showed no or little difference in the patients' backgrounds (including sex and body mass index), GERD/functional dyspepsia symptom scores, life dissatisfaction (diet, sleep, work, and mood), Short Form-8 (mental component summary) scores, and symptom improvement. In contrast, significant differences were present between grades M and A as well as between grades N and A. The overall results of our study suggest that the distinction between grade M and grade N is of little clinical significance from the viewpoint of clinical characteristics.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by GERD Society. KI received honorarium from Takeda Pharmaceutical Industry Company Limited, Otsuka Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd, AstraZeneca K.K. and EA Pharma Co.,Ltd.. KH received honorarium from Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited., Astra Zeneca K.K., Otsuka Pharmaceutical Company Limited., and Daiichi Sankyo Company Limited.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Proton pump inhibitor monotherapy is effective to attenuate dyspepsia symptoms associated with gastroesophageal reflux disease: a multicenter prospective observational study.J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jun;54(6):492-500. doi: 10.1007/s00535-019-01546-0. Epub 2019 Jan 23. J Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30673836
-
Irsogladine maleate and rabeprazole in non-erosive reflux disease: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 28;21(16):5023-31. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i16.5023. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25945018 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
More severe upper gastrointestinal symptoms associated with non-erosive reflux disease than with erosive gastroesophageal reflux disease during maintenance proton pump inhibitor therapy.J Gastroenterol. 2015 Mar;50(3):298-304. doi: 10.1007/s00535-014-0972-9. Epub 2014 Jun 12. J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 24919745
-
Dyspepsia and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD): is there any correlation?Acta Med Indones. 2009 Oct;41(4):222-7. Acta Med Indones. 2009. PMID: 20737754 Review.
-
The pharmacotherapeutic management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021 Feb;22(2):219-227. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2020.1817385. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2021. PMID: 32893683 Review.
References
-
- Manabe, N., Matsueda, K. & Haruma, K. Epidemiological review of gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma in Asian countries. Digestion 1–8 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

