VanA-Enterococcus faecalis in Poland: hospital population clonal structure and vanA mobilome
- PMID: 36057762
- PMCID: PMC9489580
- DOI: 10.1007/s10096-022-04479-4
VanA-Enterococcus faecalis in Poland: hospital population clonal structure and vanA mobilome
Abstract
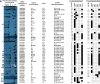
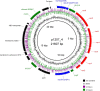
The aim of our study was to characterize the epidemiological situation concerning nosocomial vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecalis of VanA-phenotype (VREfs-VanA) in Poland by investigating their clonal relationships and the vanA-associated mobilome. One-hundred twenty-five clinical isolates of VREfs-VanA collected between 2004 and 2016 were studied by phenotypic assays, multilocus sequence typing (MLST), pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE), PCR detection of plasmid-specific genes, and Tn1546 structure and localization mapping. Selected isolates were subjected to PFGE-S1, Southern hybridization, genomic sequencing and conjugation experiments. The majority of isolates (97.6%) belonged to clonal complexes CC2 and CC87 of E. faecalis. All isolates were resistant to vancomycin and teicoplanin, and resistance to ciprofloxacin and aminoglycosides (high level) was very prevalent in this group. VanA phenotype was associated with 16 types of Tn1546, carrying insertion sequences IS1216, ISEfa4, IS1251 and IS1542, located on repUS1pVEF1, rep1pIP501, rep2pRE25, rep9pAD1/pTEF2/pCF10 and rep6pS86 replicons. The most common Tn1546 B- and BB-type transposons, harbouring one or two copies of IS1216, were inserted between rep18ap200B and repUS1pVEF1 genes and located on ~ 20 kb and 150-200 kb plasmids. VREfs-VanA in Poland represent a polyclonal group, indicating a number of acquisitions of the vanA determinant. The repUS1pVEF1-vanA plasmids, unique for Poland, were the main factor beyond the acquisition of vancomycin resistance by E. faecalis, circulating in Polish hospitals.
Keywords: Enterococcus faecalis; HAI; Plasmid; Tn1546; VRE.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (2020) Antimicrobial resistance in the EU/EEA (EARS-Net) - Annual Epidemiological Report 2019. ECDC, Stockholm
-
- Kuch A, Willems RJ, Werner G, Coque TM, Hammerum AM, Sundsfjord A, Klare I, Ruiz-Garbajosa P, Simonsen GS, van Luit-Asbroek M, Hryniewicz W, Sadowy E. Insight into antimicrobial susceptibility and population structure of contemporary human Enterococcus faecalis isolates from Europe. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67:551–558. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkr544. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

