A modified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for dengue: development, evaluation and proposal for use in clinical trials
- PMID: 36057771
- PMCID: PMC9441074
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-022-07705-8
A modified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for dengue: development, evaluation and proposal for use in clinical trials
Abstract
Background: Dengue is a neglected tropical disease, for which no therapeutic agents have shown clinical efficacy to date. Clinical trials have used strikingly variable clinical endpoints, which hampers reproducibility and comparability of findings. We investigated a delta modified Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (delta mSOFA) score as a uniform composite clinical endpoint for use in clinical trials investigating therapeutics for moderate and severe dengue.
Methods: We developed a modified SOFA score for dengue, measured and evaluated its performance at baseline and 48 h after enrolment in a prospective observational cohort of 124 adults admitted to a tertiary referral hospital in Vietnam with dengue shock. The modified SOFA score included pulse pressure in the cardiovascular component. Binary logistic regression, cox proportional hazard and linear regression models were used to estimate association between mSOFA, delta mSOFA and clinical outcomes.
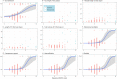
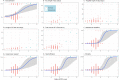
Results: The analysis included 124 adults with dengue shock. 29 (23.4%) patients required ICU admission for organ support or due to persistent haemodynamic instability: 9/124 (7.3%) required mechanical ventilation, 8/124 (6.5%) required vasopressors, 6/124 (4.8%) required haemofiltration and 5/124 (4.0%) patients died. In univariate analyses, higher baseline and delta (48 h) mSOFA score for dengue were associated with admission to ICU, requirement for organ support and mortality, duration of ICU and hospital admission and IV fluid use.
Conclusions: The baseline and delta mSOFA scores for dengue performed well to discriminate patients with dengue shock by clinical outcomes, including duration of ICU and hospital admission, requirement for organ support and death. We plan to use delta mSOFA as the primary endpoint in an upcoming host-directed therapeutic trial and investigate the performance of this score in other phenotypes of severe dengue in adults and children.
Keywords: Clinical trial endpoint; Delta SOFA; Dengue; Modified SOFA; SOFA; Shock; Vietnam.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Geneva: World Health Organization. Dengue: guidelines for diagnosis, treatment, prevention and control: new edition. Geneva; 2009. 1–144pp. http://www.who.int/tdr/publications/documents/dengue-diagnosis.pdf?ua=1 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

