Decoy Exosomes Offer Protection Against Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity
- PMID: 36058003
- PMCID: PMC9661835
- DOI: 10.1002/advs.202203505
Decoy Exosomes Offer Protection Against Chemotherapy-Induced Toxicity
Abstract
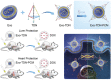
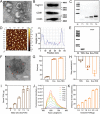
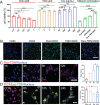
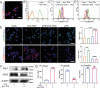
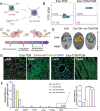
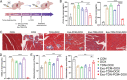
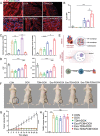
Cancer patients often face severe organ toxicity caused by chemotherapy. Among these, chemotherapy-induced hepatotoxicity and cardiotoxicity are the main causes of death of cancer patients. Chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity even creates a new discipline termed "cardio-oncology". Therefore, relieving toxicities induced by chemotherapy has become a key issue for improving the survival and quality of life in cancer patients. In this work, mesenchymal stem cell exosomes with the "G-C" abundant tetrahedral DNA nanostructure (TDN) are modified to form a decoy exosome (Exo-TDN). Exo-TDN reduces DOX-induced hepatotoxicity as the "G-C" base pairs scavenge DOX. Furthermore, Exo-TDN with cardiomyopathic peptide (Exo-TDN-PCM) is engineered for specific targeting to cardiomyocytes. Injection of Exo-TDN-PCM significantly reduces DOX-induced cardiotoxicity. Interestingly, Exo-TDN-PCM can also promote macrophage polarization into the M2 type for tissue repair. In addition, those decoy exosomes do not affect the anticancer effects of DOX. This decoy exosome strategy serves as a promising therapy to reduce chemo-induced toxicity.
Keywords: cardio-oncology; cardiotoxicity; chemotherapy; exosome; tetrahedral DNA nanostructure.
© 2022 The Authors. Advanced Science published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Sung H., Ferlay J., Siegel R. L., Laversanne M., Soerjomataram I., Jemal A., Bray F., CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209. - PubMed
-
- Zhao R., Liu X., Yang X., Jin B., Shao C., Kang W., Tang R., Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1801304. - PubMed
-
- Li L., Takemura G., Li Y., Miyata S., Esaki M., Okada H., Kanamori H., Khai N. C., Maruyama R., Ogino A., Minatoguchi S., Fujiwara T., Fujiwara H., Circulation 2006, 113, 535. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 21977024/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 21601046/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 31971304/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- B2021201038/Science Fund for Creative Research Groups of Nature Science Foundation of Hebei Province
- 2021B1515120065/Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation
- 19JCZDJC64100/Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Basic Research Cooperation Project
- DXK201916/Cross-Disciplinary Project of Hebei University
- E2018100002/One Hundred Talent Project of Hebei Province
- 81873493/National Science Foundation of China
- 82170271/National Science Foundation of China
- 204200510017/Henan Talents Program
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
