Dopamine and norepinephrine are embracing their immune side and so should we
- PMID: 36058009
- PMCID: PMC10481402
- DOI: 10.1016/j.conb.2022.102626
Dopamine and norepinephrine are embracing their immune side and so should we
Abstract
While the history of neuroimmunology is long, the explicit study of neuroimmune communication, and particularly the role of catecholamines in neuroimmunity, is still emerging. Recent studies have shown that catecholamines, norepinephrine, epinephrine, and dopamine, are central to multiple complex mechanisms regulating immune function. These studies show that catecholamines can be released from both the nervous system and directly from immune cells, mediating both autocrine and paracrine signaling. This commentary highlights the importance of catecholaminergic immunomodulation and discusses new considerations needed to study the role of catecholamines in immune homeostasis to best leverage their contribution to disease processes for the development of new therapeutic approaches.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement Nothing declared.
Figures
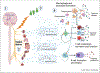
References
-
- Iversen SD, Iversen LL: Dopamine: 50 years in perspective. Trends Neurosci 2007, 30:188–193. - PubMed
-
- Snyder SH: Turning off neurotransmitters. Cell 2006, 125: 13–15. - PubMed
-
- Valenstein ES: The discovery of chemical neurotransmitters. Brain Cognit 2002, 49:73–95. - PubMed
-
- Borovikova LV, et al. : Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 2000, 405:458–462. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

