First-in-Human Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of a Rapidly Developed SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Antibody, AOD01, in Healthy Adults
- PMID: 36058990
- PMCID: PMC9441134
- DOI: 10.1007/s40121-022-00681-1
First-in-Human Study to Evaluate Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of a Rapidly Developed SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutic Antibody, AOD01, in Healthy Adults
Abstract
Introduction: AOD01 is a novel, fully human immunoglobulin (Ig) G1 neutralizing monoclonal antibody that was developed as a therapeutic against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus type 2 (SARS-CoV-2). This first-in-human study assessed safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics of AOD01 in healthy volunteers.
Methods: Intravenous doses of AOD01 were evaluated in escalating cohorts [four single-dose cohorts (2, 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg) and one two-dose cohort (two doses of 20 mg/kg, 24 h apart)].
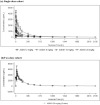
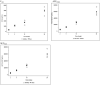
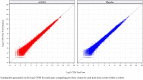
Results: Twenty-three subjects were randomized to receive AOD01 or a placebo in blinded fashion. A total of 34 treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were reported; all were mild in severity. Related events (headache and diarrhea) were reported in one subject each. No event of infusion reactions, serious adverse event (SAE), or discontinuation due to AE were reported. The changes in laboratory parameters, vital signs, and electrocardiograms were minimal. Dose-related exposure was seen from doses 2 to 20 mg/kg as confirmed by Cmax and AUC0-tlast. The median Tmax was 1.5-3 h. Clearance was dose independent. Study results revealed long half-lives (163-465 h). Antidrug antibodies (ADA) to AOD01 were not detected among subjects, except in one subject of the two-dose cohort on day 92. Sustained ex vivo neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 was recorded until day 29 with single doses from 2 to 20 mg/kg and until day 43 with two doses of 20 mg/kg.
Conclusions: AOD01 was safe and well tolerated, demonstrated dose-related PK, non-immunogenic status, and sustained ex vivo neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 after single intravenous dose ranging from 2 to 20 mg/kg and two doses of 20 mg/kg and show good potential for treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection. (Health Sciences Authority identifier number CTA2000119).
Keywords: AOD01; Antidrug antibodies; Neutralization antibody; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Weekly epidemiological update on COVID-19. 2022. https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/weekly-epidemiological-update-on.... Accessed 25 Jan 2022.
-
- Chan CEZ, Seah SGK, Chye DH, et al. The Fc-mediated effector functions of a potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody, SC31, isolated from an early convalescent COVID-19 patient, are essential for the optimal therapeutic efficacy of the antibody. PLoS ONE. 2021;16:e0253487. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0253487. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Gaudinski MR, Coates EE, Novik L, et al. Safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of the therapeutic monoclonal antibody mAb114 targeting Ebola virus glycoprotein (VRC 608): an open-label phase 1 study. Lancet. 2019;393:889–898. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30036-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous