Integrative analyses of mRNA and microRNA expression profiles reveal the innate immune mechanism for the resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in Epinephelus coioides
- PMID: 36059501
- PMCID: PMC9437975
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.982973
Integrative analyses of mRNA and microRNA expression profiles reveal the innate immune mechanism for the resistance to Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection in Epinephelus coioides
Abstract
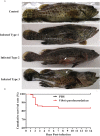
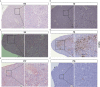
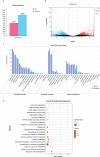
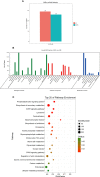
Vibrio parahaemolyticus, as one of the main pathogens of marine vibriosis, has brought huge losses to aquaculture. However, the interaction mechanism between V. parahaemolyticus and Epinephelus coioides remains unclear. Moreover, there is a lack of comprehensive multi-omics analysis of the immune response of grouper spleen to V. parahaemolyticus. Herein, E. coioides was artificially injected with V. parahaemolyticus, and it was found that the mortality was 16.7% in the early stage of infection, and accompanied by obvious histopathological lesions in the spleen. Furthermore, 1586 differentially expressed genes were screened by mRNA-seq. KEGG analysis showed that genes were significantly enriched in immune-related pathways, Acute-phase immune response, Apoptosis, Complement system and Cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction. As for miRNA-seq analysis, a total of 55 significantly different miRNAs were identified. Further functional annotation analysis indicated that the target genes of differentially expressed miRNAs were enriched in three important pathways (Phosphatidylinositol signaling system, Lysosome and Focal adhesions). Through mRNA-miRNA integrated analysis, 1427 significant miRNA-mRNA pairs were obtained and "p53 signaling pathway", "Intestinal immune network for IgA production" were considered as two crucial pathways. Finally, miR-144-y, miR-497-x, novel-m0459-5p, miR-7133-y, miR-378-y, novel-m0440-5p and novel-m0084-3p may be as key miRNAs to regulate immune signaling pathways via the miRNA-mRNA interaction network. The above results suggest that the mRNA-miRNA integrated analysis not only sheds new light on the molecular mechanisms underlying the interaction between host and V. parahaemolyticus but also provides valuable and new insights into resistance to vibrio infection.
Keywords: Epinephelus coioides; Vibrio parahaemolyticus; histopathological lesions; immune response; mRNA-seq; miRNA-seq.
Copyright © 2022 Qiao, Lu, Xu, Deng, Lai, Wu, Lin, Zhang and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic analysis of microRNAs-mRNAs regulating innate immune response of zebrafish larvae against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Aug;91:333-342. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.05.050. Epub 2019 May 23. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31129189
-
23S rRNA from Vibrio parahaemolyticus regulates the innate immune response via recognition by TLR13 in orange-spotted grouper (Epinephelus coioides).Dev Comp Immunol. 2021 Jan;114:103837. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2020.103837. Epub 2020 Aug 23. Dev Comp Immunol. 2021. PMID: 32841623
-
Integrative mRNA-miRNA interaction analysis associated with the immune response of Epinephelus coioddes to Vibrio alginolyticus infection.Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019 Jul;90:404-412. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2019.05.006. Epub 2019 May 8. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31077847
-
Circulating miRNAs involved in the immune response of the European seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax).Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025 May;160:110232. doi: 10.1016/j.fsi.2025.110232. Epub 2025 Feb 24. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40010615 Review.
-
RNA-Seq Revealed a Circular RNA-microRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Hantaan Virus Infection.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020 Mar 13;10:97. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00097. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32232013 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA Regulation in Infectious Diseases and Its Potential as a Biosensor in Future Aquaculture Industry: A Review.Molecules. 2023 May 26;28(11):4357. doi: 10.3390/molecules28114357. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37298833 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

