MX2: Identification and systematic mechanistic analysis of a novel immune-related biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus
- PMID: 36059547
- PMCID: PMC9433551
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.978851
MX2: Identification and systematic mechanistic analysis of a novel immune-related biomarker for systemic lupus erythematosus
Abstract
Background: Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) is an autoimmune disease that involves multiple organs. However, the current SLE-related biomarkers still lack sufficient sensitivity, specificity and predictive power for clinical application. Thus, it is significant to explore new immune-related biomarkers for SLE diagnosis and development.
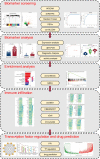
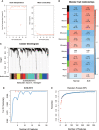
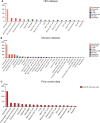
Methods: We obtained seven SLE gene expression profile microarrays (GSE121239/11907/81622/65391/100163/45291/49454) from the GEO database. First, differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were screened using GEO2R, and SLE biomarkers were screened by performing WGCNA, Random Forest, SVM-REF, correlation with SLEDAI and differential gene analysis. Receiver operating characteristic curves (ROCs) and AUC values were used to determine the clinical value. The expression level of the biomarker was verified by RT‒qPCR. Subsequently, functional enrichment analysis was utilized to identify biomarker-associated pathways. ssGSEA, CIBERSORT, xCell and ImmuCellAI algorithms were applied to calculate the sample immune cell infiltration abundance. Single-cell data were analyzed for gene expression specificity in immune cells. Finally, the transcriptional regulatory network of the biomarker was constructed, and the corresponding therapeutic drugs were predicted.
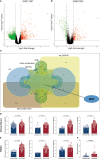
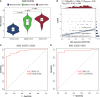
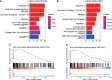
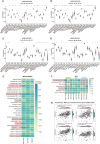
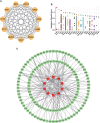
Results: Multiple algorithms were screened together for a unique marker gene, MX2, and expression analysis of multiple datasets revealed that MX2 was highly expressed in SLE compared to the normal group (all P < 0.05), with the same trend validated by RT‒qPCR (P = 0.026). Functional enrichment analysis identified the main pathway of MX2 promotion in SLE as the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway (NES=2.492, P < 0.001, etc.). Immuno-infiltration analysis showed that MX2 was closely associated with neutrophils, and single-cell and transcriptomic data revealed that MX2 was specifically expressed in neutrophils. The NOD-like receptor signaling pathway was also remarkably correlated with neutrophils (r >0.3, P < 0.001, etc.). Most of the MX2-related interacting proteins were associated with SLE, and potential transcription factors of MX2 and its related genes were also significantly associated with the immune response.
Conclusion: Our study found that MX2 can serve as an immune-related biomarker for predicting the diagnosis and disease activity of SLE. It activates the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway and promotes neutrophil infiltration to aggravate SLE.
Keywords: MX2; biomarker; immune infiltration; machine learning; systemic lupus erythematosus.
Copyright © 2022 Meng, Cheng, Lu, Tan, Jia and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

