Type 2 Inflammation Contributes to Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis
- PMID: 36059592
- PMCID: PMC9428921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xjidi.2022.100131
Type 2 Inflammation Contributes to Skin Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis
Abstract
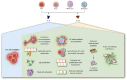
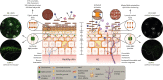
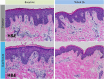
Skin barrier dysfunction, a defining feature of atopic dermatitis (AD), arises from multiple interacting systems. In AD, skin inflammation is caused by host-environment interactions involving keratinocytes as well as tissue-resident immune cells such as type 2 innate lymphoid cells, basophils, mast cells, and T helper type 2 cells, which produce type 2 cytokines, including IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, and IL-31. Type 2 inflammation broadly impacts the expression of genes relevant for barrier function, such as intracellular structural proteins, extracellular lipids, and junctional proteins, and enhances Staphylococcus aureus skin colonization. Systemic anti‒type 2 inflammation therapies may improve dysfunctional skin barrier in AD.
Keywords: AD, atopic dermatitis; AMP, antimicrobial peptide; CLDN, claudin; FFA, free fatty acid; ILC2, type 2 innate lymphoid cell; Jaki, Jak inhibitor; K, keratin; KC, keratinocyte; MMP, matrix metalloproteinase; NMF, natural moisturizing factor; PAR, protease-activated receptor; PDE-4, phosphodiesterase-4; SC, stratum corneum; SG, stratum granulosum; TCI, topical calcineurin inhibitor; TCS, topical corticosteroid; TEWL, transepidermal water loss; TJ, tight junction; TLR, toll-like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TYK, tyrosine kinase; Th, T helper; ZO, zona occludens; hBD, human β-defensin.
© 2022 The Authors.
Figures


References
-
- Akaiwa M., Yu B., Umeshita-Suyama R., Terada N., Suto H., Koga T., et al. Localization of human interleukin 13 receptor in non-haematopoietic cells. Cytokine. 2001;13:75–84. - PubMed
-
- Akdis C.A. Does the epithelial barrier hypothesis explain the increase in allergy, autoimmunity and other chronic conditions? Nat Rev Immunol. 2021;21:739–751. - PubMed
-
- Amano W., Nakajima S., Kunugi H., Numata Y., Kitoh A., Egawa G., et al. The Janus kinase inhibitor JTE-052 improves skin barrier function through suppressing signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 signaling. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015;136:667–677.e7. - PubMed
-
- Anagawa-Nakamura A., Ryoke K., Yasui Y., Shoda T., Sugai S. Effects of delgocitinib ointment 0.5% on the normal mouse skin and epidermal tight junction proteins in comparison with topical corticosteroids. Toxicol Pathol. 2020;48:1008–1016. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

