Heterologous Prime-boost of SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine and mRNA BNT162b2 among Healthy Thai Adolescents
- PMID: 36059600
- PMCID: PMC9422341
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jvacx.2022.100211
Heterologous Prime-boost of SARS-CoV-2 inactivated vaccine and mRNA BNT162b2 among Healthy Thai Adolescents
Abstract
Background: Heterologous prime-boost SARS-CoV-2 vaccination is a widely accepted strategy during the COVID-19 pandemic, which generated a superior immune response than homologous vaccination strategy.
Objective: To describe immunogenicity of heterologous prime-boost vaccination with inactivated vaccine, CoronaVac, followed by BNT162b2 and 5-month booster dose with BNT162b2 in healthy Thai adolescents.
Methods: Adolescents aged 12-18 years were randomized 1:1:1:1 to receive CoronaVac (SV) followed by BNT162b2 (PZ) 30 or 20 µg at either 3- or 6-week interval (SV3w/PZ30µg, SV3w/PZ20µg, SV6w/PZ30µg or SV6w/PZ20µg). During the Omicron-predominant period, participants were offered a BNT162b2 booster dose 30, 15, or 10 µg. Immunogenicity was determined using IgG antibody against spike-receptor-binding domain of wild type(anti-S-RBD IgG) and surrogate virus neutralization test(sVNT) against Delta variant at 14 days and 5 months after the 2nd dose. Neutralization tests(sVNT and pseudovirus neutralization test; pVNT) against Omicron strain were tested pre- and 14 days post-booster dose.
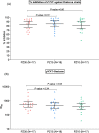
Results: In October 2021, 76 adolescents with a median age of 14.3 years (IQR 12.7-16.0) were enrolled: 20 in SV3w/PZ30µg; 17 in SV3w/PZ20µg; 20 in SV6w/PZ30µg; 19 in SV6w/PZ20µg. At day 14, the geometric mean(GM) of anti-S-RBD IgG in SV3w/PZ30µg was 4713 (95 %CI 4127-5382) binding-antibody unit (BAU)/ml, while geometric mean ratio(GMR) was 1.28 (1.09-1.51) in SV6w/PZ30µg. The GMs of sVNT against Delta variants at day 14 among participants in SV3w/PZ30µg and SV6wk/PZ30µg arm were 95.3 % and 99.7 %inhibition, respectively. At 5 months, GMs of sVNT against Delta variants in SV3w/PZ30µg were significantly declined to 47.8 % but remained at 89.0 % inhibition among SV6w/PZ30µg arm. In April 2022, 52 adolescents received a BNT162b2 booster dose. Proportion of participants with sVNT against Omicron strain > 80 %inhibition was significantly increased from 3.8 % pre-booster to 67 % post-booster. Proportion of participants with pVNT ID50 > 185 was 42 % at 14 days post 2nd dose and 88 % post booster, respectively.
Conclusions: Heterologous prime-boost vaccination with CoronaVac followed by BNT162b2 induced high neutralizing titer against SARS-CoV-2 Delta strain. After 5-month interval, booster with BNT162b2 induced high neutralizing titer against Omicron strain.Thai Clinical Trials Registry (thaiclinicaltrials.org): TCTR20210923012.
Keywords: Adolescent; Anti-SARS-CoV-2 IgG; BAU, Binding-antibody unit; BNT162b2 vaccine; Booster dose; CMI, Cell-mediated immune response; CoronaVac vaccine; ELISpot, Enzyme-linked immunospot; GM, Geometric mean; GMR, Geometric mean ratio; ID50, Neutralization dilution for 50% pseudovirus inhibition; Neutralizing antibody titer; PBMC, Peripheral blood mononuclear cell; S-RBD, Spike receptor binding domain; SARS-CoV-2 vaccine; SFU, Spot forming unit; pVNT, Pseudovirus neutralization test; sVNT, Surrogate virus neutralization test.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures



References
-
- Wanlapakorn N, Yorsaeng R, Phowatthanasathian H, Suntronwong N, Kanokudom S, Sudhinaraset N, et al. Immunogenicity of heterologous prime/boost inactivated and mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. medRxiv 2021:2021.11.20.21266644. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.20.21266644.
-
- Jantarabenjakul W., Sodsai P., Chantasrisawad N., Jitsatja A., Ninwattana S., Thippamom N., et al. Dynamics of Neutralizing Antibody and T-Cell Responses to SARS-CoV-2 and Variants of Concern after Primary Immunization with CoronaVac and Booster with BNT162b2 or ChAdOx1 in Health Care Workers. Vaccines. 2022;10(5):639. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

