Study protocol for a prospective, open-label, single-arm, phase II study on the combination of tislelizumab, nab-paclitaxel, gemcitabine, and concurrent radiotherapy as the induction therapy for patients with locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer
- PMID: 36059628
- PMCID: PMC9434272
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.879661
Study protocol for a prospective, open-label, single-arm, phase II study on the combination of tislelizumab, nab-paclitaxel, gemcitabine, and concurrent radiotherapy as the induction therapy for patients with locally advanced and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer
Abstract
Background: Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) is a fatal malignancy with a low resection rate. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy (RT) are the main treatment approaches for patients with advanced pancreatic cancer, and neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy is considered a promising strategy to increase the resection rate. Recently, immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy has shown remarkable efficacy in several cancers. Therefore, the combination of ICI, chemotherapy, and concurrent radiotherapy is promising for patients with potentially resectable pancreatic cancer, mainly referring to locally advanced (LAPC) and borderline resectable pancreatic cancer (BRPC), to increase the chances of conversion to surgical resectability and prolong survival. This study aims to introduce the design of a clinical trial.
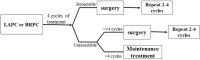
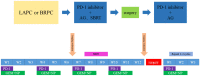
Methods: This is an open-label, single-arm, and single-center phase II trial. Patients with pathologically and radiographically confirmed LAPC or BRPC without prior anti-cancer treatment or severe morbidities will be enrolled. All patients will receive induction therapy and will be further evaluated by the Multiple Disciplinary Team (MDT) for the possibility of surgery. The induction therapy consists of up to four cycles of gemcitabine 1,000 mg/m2 and nab-paclitaxel 125 mg/m2 via intravenous (IV) infusion on days 1 and 8, along with tislelizumab (a PD-1 monoclonal antibody) 200 mg administered through IV infusion on day 1 every 3 weeks, concurrently with stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) during the third cycle of treatment. After surgery, patients without progression will receive another two to four cycles of adjuvant therapy with gemcitabine, nab-paclitaxel, and tislelizumab. The primary objectives are objective response rate (ORR) and the R0 resection rate. The secondary objectives are median overall survival (mOS), median progression free survival (mPFS), disease control rate (DCR), pathological grade of tumor tissue after therapy, and adverse reactions. Besides, we expect to explore the value of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) in predicting tumor response to induction therapy and survival outcome of patients.
Discussion: This is a protocol for a clinical trial that attempts to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the combination of anti-PD-1 antibody plus chemotherapy and radiotherapy as the induction therapy for LAPC and BRPC. The results of this phase II study will provide evidence for the clinical practice of this modality.
Clinical trial registration: http://www.chictr.org.cn/edit.aspx?pid=53720&htm=4, identifier ChiCTR2000032955.
Keywords: PD-1 blockade; circulating tumor DNA; clinical protocol; induction therapy; pancreatic cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Lu, Zhu, Kong, Yang, Zhu, Wang, Tang, Chen, Li, He, Li, Qiu, Gu, Chen, Meng, Liu, Qiu and Du.
Conflict of interest statement
Author DC was employed by Jiangsu Simcere Diagnostics Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources