Relationship between metabolic reprogramming and drug resistance in breast cancer
- PMID: 36059650
- PMCID: PMC9434120
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.942064
Relationship between metabolic reprogramming and drug resistance in breast cancer
Abstract
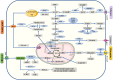
Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer death in women. At present, chemotherapy is the main method to treat breast cancer in addition to surgery and radiotherapy, but the process of chemotherapy is often accompanied by the development of drug resistance, which leads to a reduction in drug efficacy. Furthermore, mounting evidence indicates that drug resistance is caused by dysregulated cellular metabolism, and metabolic reprogramming, including enhanced glucose metabolism, fatty acid synthesis and glutamine metabolic rates, is one of the hallmarks of cancer. Changes in metabolism have been considered one of the most important causes of resistance to treatment, and knowledge of the mechanisms involved will help in identifying potential treatment deficiencies. To improve women's survival outcomes, it is vital to elucidate the relationship between metabolic reprogramming and drug resistance in breast cancer. This review analyzes and investigates the reprogramming of metabolism and resistance to breast cancer therapy, and the results offer promise for novel targeted and cell-based therapies.
Keywords: Breast cancer; drug resistance; fatty acid synthesis; glucose metabolism; metabolic reprogramming.
Copyright © 2022 Lv, Yang, Zhu, Zhai, Li, Tao and Dong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Global cancer observatory: Cancer today. Lyon, France: International Agency for Research on Cancer; (2020). Available at: http://gco.iarc.fr/2020.
-
- The Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation . Global burden of disease. (2020). Available at: http://www.healthdata.org/gbd/20192020.
-
- Gianni L, Pienkowski T, Im YH, Tseng LM, Liu MC, Lluch A, et al. 5-year analysis of neoadjuvant pertuzumab and trastuzumab in patients with locally advanced, inflammatory, or early-stage Her2-positive breast cancer (Neosphere): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised trial. Lancet Oncol (2016) 17:791–800. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(16)00163-7 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

