Pharmacological investigation of brucine anti-ulcer potential
- PMID: 36059979
- PMCID: PMC9429807
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.886433
Pharmacological investigation of brucine anti-ulcer potential
Abstract
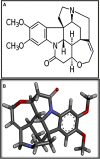
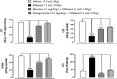
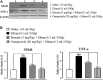
Gastric ulcer is one of the most common chronic gastrointestinal diseases characterized by a significant defect in the mucosal barrier. The current study has been conducted to evaluate the brucine anti-ulcer effect. Brucine has binding energy values ranging from -2.99 to -8.11 kcal/mol against chosen targets, according to in silico research. Brucine exhibits an inhibitory effect against Helicobacter pylori. In vivo findings revealed that brucine (3 mg/kg) showed effective results in healing ethanol-induced ulcer lesions of the gastric region in rats. Brucine showed an inhibitory effect against H+/K+-ATPase. Levels of glutathione, glutathione-s-transferase, and catalase were enhanced in the gastric rat tissue with the use of brucine, while a significant decrease in lipid peroxide levels was seen. Histopathological evaluation showed improvement in cellular architecture and a decrease in inflammatory indicators like cyclooxygenase, tumor necrosis factor, and nuclear factor kappa B expression, validated through immunohistochemistry, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and Western blot techniques. In the reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, brucine decreased H+/K+-ATPase mRNA levels. This study reveals that brucine possesses stable binding affinities against selected targets. Brucine exhibits an anti-ulcer effect, mediated via anti-H. pylori, H+/K+-ATPase inhibition, and antioxidant and anti-inflammatory pathways.
Keywords: H+/K+-ATPase; anti-H. pylori; anti-inflammatory; anti-ulcer; antioxidant; brucine.
Copyright © 2022 Noman, Qazi, Rehman and Khan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures







References
-
- Abebaw M., Mishra B., Gelayee D. A. (2017). Evaluation of anti-ulcer activity of the leaf extract of Osyris Quadripartita Decne (Santalaceae) in rats. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 9 (1), 1–11. 10.2147/JEP.S125383 PubMed Abstract | 10.2147/JEP.S125383 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Al Batran R., Al-Bayaty F., Jamil Al-Obaidi M. M., Abdualkader A. M., Hadi H. A., Ali H. M. (2013). In vivo antioxidant and antiulcer activity of Parkia speciosa ethanolic leaf extract against ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats. PLoS One 8 (5), 64751. 10.1371/journal.pone.0064751 10.1371/journal.pone.0064751 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Almasaudi S. B., El-Shitany N. A., Abbas A. T., Abdel-dayem U. A., Ali S. S., Al Jaouni S. K., et al. (2016). Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antiulcer potential of Manuka Honey against gastric ulcer in rats. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 1 (1), 3643824. 10.1155/2016/3643824 10.1155/2016/3643824 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ansari S. F., Khan A. U., Qazi N. G., Shah F. A., Naeem K. (2019). In vivo, proteomic, and in- silico investigation of Sapodilla for therapeutic potential in gastrointestinal disorders. Biomed. Res. Int. 1 (1), 1–19. 10.1155/2019/4921086 10.1155/2019/4921086 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arab H. H., Salama S. A., Omar H. A., Arafa E. S. A., Maghrabi I. A. (2015). Diosmin protects against ethanol-induced gastric injury in rats: Novel anti-ulcer actions. PLoS One 10 (3), 0122417. 10.1371/journal.pone.0122417 10.1371/journal.pone.0122417 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

