New strategies for identifying and masking the bitter taste in traditional herbal medicines: The example of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction
- PMID: 36060004
- PMCID: PMC9431955
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.843821
New strategies for identifying and masking the bitter taste in traditional herbal medicines: The example of Huanglian Jiedu Decoction
Abstract
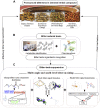
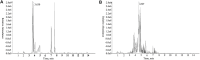
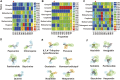
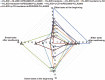
Suppressing the bitter taste of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) largely has been a major clinical challenge due to complex and diverse metabolites and high dispersion of bitter metabolites in liquid preparations. In this work, we developed a novel strategy for recognizing bitter substances, hiding their bitter taste, and elucidated the mechanism of flavor masking in TCM. Huanglian Jie-Du Decoction (HLJDD) with an intense bitter taste was studied as a typical case. UHPLC-MS/MS was used to analyze the chemical components in HLJDD, whereas the bitter substances were identified by pharmacophores. Additionally, the screening results of the pharmacophores were further validated by using experimental assays. The mask formula of HLJDD was effectively screened under the condition of clear bitter substances. Subsequently, computational chemistry, molecular docking, and infrared characterization (IR) techniques were then used to explicate the mechanism of flavor masking. Consequently, neotame, γ-CD, and mPEG2000-PLLA2000 significantly reduced the bitterness of HLJDD. Specifically, mPEG2000-PLLA2000 increased the colloid proportion in the decoction system and minimized the distribution of bitter components in the real solution. Sweetener neotame suppressed the perception of bitter taste and inhibited bitter taste receptor activation to eventually reduce the bitter taste. The γ-CD included in the decoction bound the hydrophobic groups of the bitter metabolites in real solution and "packed" all or part of the bitter metabolites into the "cavity". We established a novel approach for screening bitter substances in TCM by integrating virtual screening and experimental assays. Based on this strategy, the bitter taste masking of TCM was performed from three different aspects, namely, changing the drug phase state, component distribution, and interfering with bitter taste signal transduction. Collectively, the methods achieved a significant effect on bitter taste suppression and taste masking. Our findings will provide a novel strategy for masking the taste of TCM liquid preparation/decoction, which will in return help in improving the clinical efficacy of TCM.
Keywords: Huanglian Jie-du Decoction; bitterness; bitterness suppression; mechanism; neotame; γ-CD.
Copyright © 2022 Ke, Ma, Yang, Qiu, Wang, Han and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Combined anti-bitterness strategy for extremely bitter characteristics of Andrographis Herba decoction and mechanism].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022 Oct;47(20):5424-5433. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20220630.301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36471956 Chinese.
-
[Structure-activity relationship of coptis alkaloid bitterness inhibited by mPEG-PLLA].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020 Jul;45(13):3128-3135. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20200424.301. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32726021 Chinese.
-
Deciphering the pharmacological mechanism of the Chinese formula huanglian-jie-du decoction in the treatment of ischemic stroke using a systems biology-based strategy.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015 Jun;36(6):724-33. doi: 10.1038/aps.2014.124. Epub 2015 May 4. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2015. PMID: 25937634 Free PMC article.
-
Developments in Taste-Masking Techniques for Traditional Chinese Medicines.Pharmaceutics. 2018 Sep 12;10(3):157. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10030157. Pharmaceutics. 2018. PMID: 30213035 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bitter flavors and bitter compounds in foods: identification, perception, and reduction techniques.Food Res Int. 2024 May;183:114234. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2024.114234. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Food Res Int. 2024. PMID: 38760147 Review.
Cited by
-
One of the major challenges of masking the bitter taste in medications: an overview of quantitative methods for bitterness.Front Chem. 2024 Aug 14;12:1449536. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1449536. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 39206439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sex Differences in the Bitterness Perception of an Aromatic Myrtle Bitter Liqueur and Bitter Compounds.Nutrients. 2023 Apr 23;15(9):2030. doi: 10.3390/nu15092030. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37432169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amin F., Khan S., Shah S. M. H., Rahim H., Hussain Z., Sohail M., et al. (2018). A new strategy for taste masking of azithromycin antibiotic: development, characterization, and evaluation of azithromycin titanium nanohybrid for masking of bitter taste using physisorption and panel testing studies. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 12, 3855–3866. 10.2147/DDDT.S183534 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

