Apatinib for recurrent/progressive glioblastoma multiforme: A salvage option
- PMID: 36060005
- PMCID: PMC9432461
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.969565
Apatinib for recurrent/progressive glioblastoma multiforme: A salvage option
Abstract
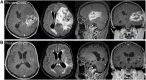
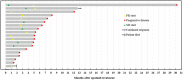
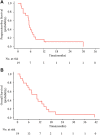
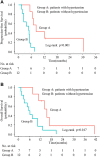
Purpose: The recurrent/progressive glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) carries a dismal prognosis and the definitive treatment strategy has not yet been established. This study aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of apatinib in recurrent/progressive GBM patients. Materials and methods: The clinical data of 19 recurrent/progressive GBM patients who received apatinib treatment from November 2015 to December 2019 at Sun Yat-sen University Cancer Center were collected retrospectively in this study. Objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR), progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), and treatment-related adverse events (AEs) were reviewed and assessed. Results: The overall ORR was 52.6%, and the DCR was 73.7%. Median PFS and OS were 5.1 and 10.4 months, respectively. The 6-month PFS and OS rates were 38.9% and 68.4%, respectively. The 12-month PFS and OS rates were 16.7% and 36.8%, respectively. The treatment-related toxicities were generally well-tolerated. The most common grade 3/4 AEs were hand-foot syndrome (36.8%) and hypertension (21.1%). Conclusion: Our study showed that apatinib therapy provided a better salvaging option for recurrent/progressive GBM patients and the toxicity was manageable.
Keywords: VEGFR; apatinib; efficacy; recurrent/progressive glioblastoma multiforme; safety.
Copyright © 2022 Zhang, Du, Deng, Zheng, Yao, Wang, Yang and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy of apatinib 250 mg combined with chemotherapy in patients with pretreated advanced breast cancer in a real-world setting.Front Oncol. 2023 Jun 16;13:1076469. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1076469. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37397355 Free PMC article.
-
Apatinib Plus Temozolomide: An Effective Salvage Treatment for Recurrent Glioblastoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Feb 4;10:601175. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.601175. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33634023 Free PMC article.
-
The Efficacy And Safety Of Apatinib Treatment For Patients With Metastatic Or Recurrent Cervical Cancer: A Retrospective Study.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019 Sep 26;13:3419-3424. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S214743. eCollection 2019. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2019. PMID: 31576114 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Apatinib for the Treatment of Advanced or Recurrent Cervical Cancer: A Single-Arm Meta-Analysis Among Chinese Patients.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 11;13:843905. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.843905. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36034824 Free PMC article.
-
Apatinib in recurrent anaplastic meningioma: a retrospective case series and systematic literature review.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020 Jul 2;21(7):583-589. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2020.1740053. Epub 2020 Mar 25. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 32212907 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy and Safety of Apatinib in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma.Drugs R D. 2023 Sep;23(3):239-244. doi: 10.1007/s40268-023-00429-3. Epub 2023 Jul 19. Drugs R D. 2023. PMID: 37466833 Free PMC article.
-
From signalling pathways to targeted therapies: unravelling glioblastoma's secrets and harnessing two decades of progress.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Oct 20;8(1):400. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01637-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37857607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Personalized Medicine in Brain Gliomas: Targeted Therapy, Patient-Derived Tumor Models (Review).Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2023;15(3):61-71. doi: 10.17691/stm2023.15.3.07. Epub 2023 May 28. Sovrem Tekhnologii Med. 2023. PMID: 38435477 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azad N. S., Aragon-Ching J. B., Dahut W. L., Gutierrez M., Figg W. D., Jain L., et al. (2009). Hand-foot skin reaction increases with cumulative sorafenib dose and with combination anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 15 (4), 1411–1416. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1141 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

