Therapeutic targets by traditional Chinese medicine for ischemia-reperfusion injury induced apoptosis on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
- PMID: 36060007
- PMCID: PMC9437626
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.934256
Therapeutic targets by traditional Chinese medicine for ischemia-reperfusion injury induced apoptosis on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases
Abstract
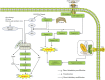
Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has a significant role in treating and preventing human diseases. Ischemic heart and cerebrovascular injuries are two types of diseases with different clinical manifestations with high prevalence and incidence. In recent years, it has been reported that many TCM has beneficial effects on ischemic diseases through the inhibition of apoptosis, which is the key target to treat myocardial and cerebral ischemia. This review provides a comprehensive summary of the mechanisms of various TCMs in treating ischemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases through anti-apoptotic targets and pathways. However, clinical investigations into elucidating the pharmacodynamic ingredients of TCM are still lacking, which should be further demystified in the future. Overall, the inhibition of apoptosis by TCM may be an effective strategy for treating ischemic cardio-cerebrovascular diseases.
Keywords: apoptosis; cerebral ischemia; molecular mechanisms; myocardial ischemia; traditional Chinese medicine.
Copyright © 2022 Cheng, Hu, Liu, Tibenda, Wang and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Argüelles S., Guerrero-Castilla A., Cano M., Muñoz M. F., Ayala A. (2019). Advantages and disadvantages of apoptosis in the aging process. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1443, 20–33. 10.1111/nyas.14020 PubMed Abstract | 10.1111/nyas.14020 | Google Scholar - DOI - PubMed
-
- Battaglini D., Robba C., Lopes da Silva A., Dos Santos Samary C., Leme Silva P., Dal Pizzol F., et al. (2020). Brain-heart interaction after acute ischemic stroke. Crit. Care 24, 163. 10.1186/s13054-020-02885-8 PubMed Abstract | 10.1186/s13054-020-02885-8 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cao J., Wang K., Lei L., Bai L., Liang R., Qiao Y., et al. (2020). Astragaloside and/or hydroxysafflor yellow A attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced cultured brain microvessel endothelial cell death through downregulation of PHLPP-1. Evid. Based. Complement. Altern. Med. 2020, 3597527. 10.1155/2020/3597527 10.1155/2020/3597527 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chang L. L., Li C., Li Z. L., Wei Z. L., Jia X. B., Pang S. T., et al. (2020). Carthamus tinctorius L. Extract ameliorates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats by regulating matrix metalloproteinases and apoptosis. Indian J. Pharmacol. 52, 108–116. 10.4103/ijp.IJP_400_18 PubMed Abstract | 10.4103/ijp.IJP_400_18 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen J., Wei J., Orgah J., Zhu Y., Ni J., Li L., et al. (2019a). Cardioprotective effect of Danhong injection against myocardial infarction in rats is critically contributed by MicroRNAs. Evidence-based complementary Altern. Med. 2019, 4538985. 10.1155/2019/4538985 10.1155/2019/4538985 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

