Preparation of RNAs with non-canonical 5' ends using novel di- and trinucleotide reagents for co-transcriptional capping
- PMID: 36060251
- PMCID: PMC9437278
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.854170
Preparation of RNAs with non-canonical 5' ends using novel di- and trinucleotide reagents for co-transcriptional capping
Abstract
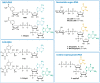
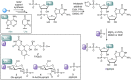
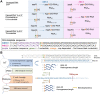
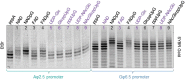
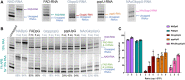
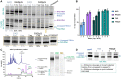
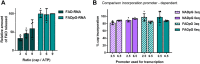
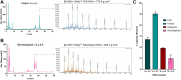
Many eukaryotic and some bacterial RNAs are modified at the 5' end by the addition of cap structures. In addition to the classic 7-methylguanosine 5' cap in eukaryotic mRNA, several non-canonical caps have recently been identified, including NAD-linked, FAD-linked, and UDP-glucose-linked RNAs. However, studies of the biochemical properties of these caps are impaired by the limited access to in vitro transcribed RNA probes of high quality, as the typical capping efficiencies with NAD or FAD dinucleotides achieved in the presence of T7 polymerase rarely exceed 50%, and pyrimidine derivatives are not incorporated because of promoter sequence limitations. To address this issue, we developed a series of di- and trinucleotide capping reagents and in vitro transcription conditions to provide straightforward access to unconventionally capped RNAs with improved 5'-end homogeneity. We show that because of the transcription start site flexibility of T7 polymerase, R1ppApG-type structures (where R1 is either nicotinamide riboside or riboflavin) are efficiently incorporated into RNA during transcription from dsDNA templates containing both φ 6.5 and φ 2.5 promoters and enable high capping efficiencies (∼90%). Moreover, uridine-initiated RNAs are accessible by transcription from templates containing the φ 6.5 promoter performed in the presence of R2ppUpG-type initiating nucleotides (where R2 is a sugar or phosphate moiety). We successfully employed this strategy to obtain several nucleotide-sugar-capped and uncapped RNAs. The capping reagents developed herein provide easy access to chemical probes to elucidate the biological roles of non-canonical RNA 5' capping.
Keywords: FAD; In vitro transcription; NAD; RNA cap; UDP-glucose; dinucleotide; trinucleotide.
Copyright © 2022 Depaix, Grudzien-Nogalska, Fedorczyk, Kiledjian, Jemielity and Kowalska.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Noncanonical RNA-capping: Discovery, mechanism, and physiological role debate.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019 Mar;10(2):e1512. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1512. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2019. PMID: 30353673 Review.
-
In vitro transcription and capping of Gaussia luciferase mRNA followed by HeLa cell transfection.J Vis Exp. 2012 Mar 26;(61):3702. doi: 10.3791/3702. J Vis Exp. 2012. PMID: 22473375 Free PMC article.
-
CapZyme-Seq Comprehensively Defines Promoter-Sequence Determinants for RNA 5' Capping with NAD<sup/>Mol Cell. 2018 May 3;70(3):553-564.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.03.014. Epub 2018 Apr 19. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29681497 Free PMC article.
-
The mechanism of RNA 5′ capping with NAD+, NADH and desphospho-CoA.Nature. 2016 Jul 21;535(7612):444-7. doi: 10.1038/nature18622. Epub 2016 Jul 6. Nature. 2016. PMID: 27383794 Free PMC article.
-
The expanding field of non-canonical RNA capping: new enzymes and mechanisms.R Soc Open Sci. 2021 May 19;8(5):201979. doi: 10.1098/rsos.201979. R Soc Open Sci. 2021. PMID: 34017598 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
DNA-terminus-dependent transcription by T7 RNA polymerase and its C-helix mutants.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Aug 12;52(14):8443-8453. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae593. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38979568 Free PMC article.
-
Application of Mammalian Nudix Enzymes to Capped RNA Analysis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Sep 11;17(9):1195. doi: 10.3390/ph17091195. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39338357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trinucleotide mRNA Cap Analogue N6-Benzylated at the Site of Posttranscriptional m6Am Mark Facilitates mRNA Purification and Confers Superior Translational Properties In Vitro and In Vivo.J Am Chem Soc. 2024 Mar 27;146(12):8149-8163. doi: 10.1021/jacs.3c12629. Epub 2024 Mar 5. J Am Chem Soc. 2024. PMID: 38442005 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular exosomal RNAs are glyco-modified.Nat Cell Biol. 2025 Jun;27(6):983-991. doi: 10.1038/s41556-025-01682-1. Epub 2025 Jun 4. Nat Cell Biol. 2025. PMID: 40467769
-
Trinucleotide cap analogs with triphosphate chain modifications: synthesis, properties, and evaluation as mRNA capping reagents.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Oct 14;52(18):10788-10809. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae763. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 39248095 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

