Construction of Prognostic Risk Model of Patients with Skin Cutaneous Melanoma Based on TCGA-SKCM Methylation Cohort
- PMID: 36060650
- PMCID: PMC9436567
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4261329
Construction of Prognostic Risk Model of Patients with Skin Cutaneous Melanoma Based on TCGA-SKCM Methylation Cohort
Abstract
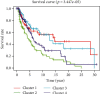
Skin cutaneous melanoma (SKCM) is a common malignant skin cancer. Early diagnosis could effectively reduce SKCM patient's mortality to a large extent. We managed to construct a model to examine the prognosis of SKCM patients. The methylation-related data and clinical data of The Cancer Gene Atlas- (TCGA-) SKCM were downloaded from TCGA database. After preprocessing the methylation data, 21,861 prognosis-related methylated sites potentially associated with prognosis were obtained using the univariate Cox regression analysis and multivariate Cox regression analysis. Afterward, unsupervised clustering was used to divide the patients into 4 clusters, and weighted correlation network analysis (WGCNA) was applied to construct coexpression modules. By overlapping the CpG sites between the clusters and turquoise model, a prognostic model was established by LASSO Cox regression and multivariate Cox regression. It was found that 9 methylated sites included cg01447831, cg14845689, cg20895058, cg06506470, cg09558315, cg06373660, cg17737409, cg21577036, and cg22337438. After constructing the prognostic model, the performance of the model was validated by survival analysis and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, and the independence of the model was verified by univariate and multivariate regression. It was represented that the prognostic model was reliable, and riskscore could be used as an independent prognostic factor in SKCM patients. At last, we combined clinical data and patient's riskscore to establish and testify the nomogram that could determine patient's prognosis. The results found that the reliability of the nomogram was relatively good. All in all, we constructed a prognostic model that could determine the prognosis of SKCM patients and screened 9 key methylated sites through analyzing data in TCGA-SKCM dataset. Finally, a prognostic nomogram was established combined with clinical diagnosed information and riskscore. The results are significant for improving the prognosis of SKCM patients in the future.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaoming Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Analysis on tumor immune microenvironment and construction of a prognosis model for immune-related skin cutaneous melanoma.Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023 May 28;48(5):671-681. doi: 10.11817/j.issn.1672-7347.2023.230069. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2023. PMID: 37539569 Free PMC article. Chinese, English.
-
Identification of m6A-related lncRNAs-based signature for predicting the prognosis of patients with skin cutaneous melanoma.SLAS Technol. 2024 Feb;29(1):100101. doi: 10.1016/j.slast.2023.08.001. Epub 2023 Aug 2. SLAS Technol. 2024. PMID: 37541541
-
Development and validation of an immune gene set-based prognostic signature in cutaneous melanoma.Future Oncol. 2021 Nov;17(31):4115-4129. doi: 10.2217/fon-2021-0104. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Future Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34291650
-
System analysis based on the pyroptosis-related genes identifes GSDMD as a novel therapy target for skin cutaneous melanoma.J Transl Med. 2023 Nov 10;21(1):801. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04513-9. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37950289 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of differential gene immune infiltration and clinical characteristics of skin cutaneous melanoma based on systems biology and drug repositioning methods to identify drug candidates for skin cutaneous melanoma.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Oct;396(10):2427-2447. doi: 10.1007/s00210-023-02461-1. Epub 2023 Apr 22. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37086280 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A novel risk model based on anoikis: Predicting prognosis and immune infiltration in cutaneous melanoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jan 16;13:1090857. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1090857. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36726781 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Analysis of the Effect of the BRAF Inhibitor Dabrafenib in 2D and 3D Cell Culture Models of Human Metastatic Melanoma Cells.In Vivo. 2024 Jul-Aug;38(4):1579-1593. doi: 10.21873/invivo.13608. In Vivo. 2024. PMID: 38936891 Free PMC article.
-
The role and prognostic value of PANoptosis-related genes in skin cutaneous melanoma.Front Immunol. 2025 Jun 6;16:1605977. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1605977. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40547036 Free PMC article.
-
Experimentally validated oxidative stress -associated prognostic signatures describe the immune landscape and predict the drug response and prognosis of SKCM.Front Immunol. 2024 Apr 10;15:1387316. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1387316. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38660305 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation-driven genes in hepatocellular carcinoma patients: insights into immune infiltration and prognostic implications.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Apr 28;12:1520380. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1520380. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40357287 Free PMC article.
References
-
- You Y. H., Lee D. H., Yoon J. H., Nakajima S., Yasui A., Pfeifer G. P. Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers are responsible for the vast majority of mutations induced by UVB irradiation in mammalian cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry . 2001;276(48):44688–44694. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M107696200. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

