Influence of Case Management Model Combined with Continuous Nursing Care on Compliance Behavior and Adverse Emotions in Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer: A Prospective Single-Center Case-Control Study
- PMID: 36060666
- PMCID: PMC9433228
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/2601852
Influence of Case Management Model Combined with Continuous Nursing Care on Compliance Behavior and Adverse Emotions in Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer: A Prospective Single-Center Case-Control Study
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Influence of Case Management Model Combined with Continuous Nursing Care on Compliance Behavior and Adverse Emotions in Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer: A Prospective Single-Center Case-Control Study.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9825948. doi: 10.1155/2023/9825948. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811286 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Aims: To ask lots of questions about finding the truth about the influence of the case management model combined with continuous nursing care on following the law behavior and negative feelings of love, hate, fear, etc. in old patients with lung scale-like cell cancer.
Materials and methods: One hundred and forty-three elderly patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung were selected for this prospective study, 10 cases were shed due to epidemic and transfer, and finally 68 cases were in the control group and 65 cases in the observation group. The differences in anxiety and depression scores, quality of life, and compliance behavior between the two groups were observed and compared.
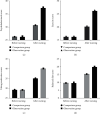
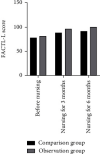
Results: After nursing, the self-rating anxiety scale (SAS) and self-rating depression scale (SDS) of the observation group were lower than those of the control group, while the social support score was significantly higher than that of the control group. The scores of psychological behavior, exercise status, drug taking, and balanced diet of the two groups were significantly improved, and the observation group was significantly improved. The scores of medical compliance behavior in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, and the mental vitality score, social interaction score, emotional restriction score, and mental status of the patients in the observation group were significantly higher than those in the control group, and the above statistics showed that the difference was statistically significant (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The use of a case management model combined with extended care significantly improved the compliance behavior and anxiety and depression of elderly patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the lung and improved the quality of life and social support.
Copyright © 2022 Aomei Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Focus on the effect of nursing care combined with cognitive intervention and functional training on negative emotion, compliance and quality of life in elderly patients with sudden deafness: A retrospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 Jun 14;103(24):e38283. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038283. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 38875427 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Psychological Intervention-Assisted Comfort Nursing Based on PERMA Model on Stress and Psychological Changes of Patients after Breast Cancer Surgery.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jun 7;2022:1853754. doi: 10.1155/2022/1853754. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9836745. doi: 10.1155/2023/9836745. PMID: 35712008 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Effects of ADOPT-Based Breathing Training Combined with Continuous Nursing on Quality of Life, Mental Health, and Self-Efficacy in Lung Cancer Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: Based on a Retrospective Cohort Study.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Apr 20;2022:4164771. doi: 10.1155/2022/4164771. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9798781. doi: 10.1155/2023/9798781. PMID: 35495891 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The effect of predictive nursing on the mental state, compliance and sleep quality of senile cervicitis: An observational study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2024 May 31;103(22):e38095. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000038095. Medicine (Baltimore). 2024. PMID: 39259125 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of psychological nursing and health education on depression, anxiety and life quality of elderly patients with lung cancer.Psychogeriatrics. 2021 Jul;21(4):521-527. doi: 10.1111/psyg.12700. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Psychogeriatrics. 2021. PMID: 33913217 Clinical Trial.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Influence of Case Management Model Combined with Continuous Nursing Care on Compliance Behavior and Adverse Emotions in Elderly Patients with Lung Cancer: A Prospective Single-Center Case-Control Study.Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Sep 27;2023:9825948. doi: 10.1155/2023/9825948. eCollection 2023. Comput Math Methods Med. 2023. PMID: 37811286 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dort J. C., Farwell D. G., Findlay M., et al. Optimal perioperative care in major head and neck cancer surgery with free flap reconstruction: a consensus review and recommendations from the enhanced recovery after surgery society. JAMA Otolaryngology. Head & Neck Surgery . 2017;143(3):292–303. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2016.2981. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Yilong W., Meilin L., Guoliang J. Consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chinese Journal of Oncology . 2002;24(6):576–578.
-
- Qiuxia W., Dan F., Cuiqun S. Study on the correlation between psychological resilience, anxiety and depression in patients with cerebral arteriovenous malformation. Nursing Research . 2018;32(22):3558–3561. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1009-6493.2018.22.019. - DOI
-
- Feng L., Jingyu X., Lin W. Effects of comprehensive nursing intervention mode on social support, quality of life and BPRS score in patients with schizophrenia. International Journal of Nursing . 2019;38(24):4191–4194.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

