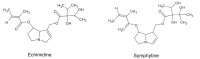Anti-inflammatory Properties of the Genus Symphytum L.: A Review
- PMID: 36060906
- PMCID: PMC9420230
- DOI: 10.5812/ijpr.123949
Anti-inflammatory Properties of the Genus Symphytum L.: A Review
Abstract
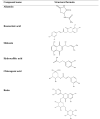
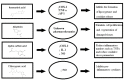
The Symphytum genus has been mainly used in traditional medicine, containing its anti-inflammatory activity. Symphytum spp.'s active components, such as allantoin, polyphenols, flavonoids, and alkaloids, can act on several intentions in the signaling pathway, constrain pro-inflammatory enzymes, reducing the construction of inflammatory chemokine's and cytokines, and decreasing oxidative stress, which afterward suppresses inflammation procedures. Preclinical and clinical trials have reported the prevailing anti-inflammatory effect of several Symphytum species. This review presents an overview of the anti-inflammatory activities of different products and bioactive constituents in this genus. The papers with the English language were gathered from 2000 to 2021. This review may provide a scientific base for establishing innovative and alternative techniques for isolating a single individual from this genus to attenuate inflammatory disorders. The Symphytum genus is waiting for researchers to develop safe and effective anti-inflammatory agents for additional investigation of other different mechanisms of action.
Keywords: Arthritis; Boraginacea; Comfrey; Inflammation; Rheumatoid; Wound Healing.
Copyright © 2022, Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Genus Curcuma and Inflammation: Overview of the Pharmacological Perspectives.Plants (Basel). 2020 Dec 30;10(1):63. doi: 10.3390/plants10010063. Plants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The genus Rosa and arthritis: Overview on pharmacological perspectives.Pharmacol Res. 2016 Dec;114:219-234. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2016.10.029. Epub 2016 Nov 2. Pharmacol Res. 2016. PMID: 27816506 Review.
-
The genus Inula and their metabolites: from ethnopharmacological to medicinal uses.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Jun 11;154(2):286-310. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.010. Epub 2014 Apr 19. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24754913
-
Symphytum officinale L.: Liquid-liquid chromatography isolation of caffeic acid oligomers and evaluation of their influence on pro-inflammatory cytokine release in LPS-stimulated neutrophils.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Nov 15;262:113169. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.113169. Epub 2020 Jul 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32739565
-
Is comfrey root more than toxic pyrrolizidine alkaloids? Salvianolic acids among antioxidant polyphenols in comfrey (Symphytum officinale L.) roots.Food Chem Toxicol. 2018 Feb;112:178-187. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2017.12.051. Epub 2017 Dec 28. Food Chem Toxicol. 2018. PMID: 29288756
Cited by
-
Antiulcer Effect of Genus Symphytum L. and Portulaca oleracea L. as Investigated on Experimental Animals.J Nutr Metab. 2024 Sep 17;2024:9208110. doi: 10.1155/2024/9208110. eCollection 2024. J Nutr Metab. 2024. PMID: 39318606 Free PMC article.
-
Recent advancement in molecular pathways and receptor targeting using natural products for wound healing activity.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jul 25. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01858-z. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40711682 Review.
-
Medicinal Plants of the Flora of Kazakhstan Used in the Treatment of Skin Diseases.Molecules. 2023 May 19;28(10):4192. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104192. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241933 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Scotti F, Decani S, Sardella A, Iriti M, Varoni EM, Lodi G. Anti-inflammatory and wound healing effects of an essential oils-based bioadhesive gel after oral mucosa biopsies: preliminary results. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2018;64(8):78–83. - PubMed
-
- Pok LSL, Shabaruddin FH, Dahlui M, Sockalingam S, Mohamed Said MS, Rosman A, et al. Clinical and economic implications of upper gastrointestinal adverse events in Asian rheumatological patients on long-term non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Int J Rheum Dis. 2018;21(5):943–51. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.13256. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Smith DB, Jacobson BH. Effect of a blend of comfrey root extract (Symphytum officinale L.) and tannic acid creams in the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee: randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, multiclinical trials. J Chiropr Med. 2011;10(3):147–56. doi: 10.1016/j.jcm.2011.01.003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous