Protective Effect of Tilia americana var. mexicana Against Kainic Acid-induced Damage in Brain, Liver, and Kidney: Behavioral and Biochemical Changes
- PMID: 36060909
- PMCID: PMC9420231
- DOI: 10.5812/ijpr-126914
Protective Effect of Tilia americana var. mexicana Against Kainic Acid-induced Damage in Brain, Liver, and Kidney: Behavioral and Biochemical Changes
Abstract
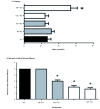
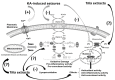
Tiliaamericana var. mexicana (Tilia) possesses anticonvulsant, antioxidant, neuroprotective, and hepatoprotective activities. The spectrum of anticonvulsant activity in status epilepticus models has not been sufficiently explored. We evaluated the effects of ethyl acetate (EAc), and methanol (ME) extracts on kainic acid (KA)-induced seizures by measuring rats'behavior (severity and latency) and lipoperoxidation in different brain areas (cerebellum, brain hemispheres, cortex, and medulla), kidneys, and liver. Male Wistar rats were administered KA (10 mg/kg, i.p.) after three days of pretreatment with Tilia extract (100 mg/kg). The EAc and ME Tilia extracts significantly decreased the severity of phase 1 and phase 2 seizures, respectively. The ME Tilia extract increased the latency to seizure (27 ± 2 min) compared to the control (13 ± 2 min). The ME and EAc Tilia extracts significantly prevented the increased lipid peroxidation caused by KA-induced seizures in the cerebellum, brain hemispheres, cortex, medulla, liver, and kidneys. The vehicle olive oil (OO) also showed anticonvulsant effects, decreasing the severity of seizures to phase 3 and lipoperoxidation levels in the cerebellum, brain hemispheres, cortex, medulla, liver, and kidneys. The anticonvulsant activity of Tilia is mediated by antioxidant effects in central and systemic areas that involve synergistic interactions among the chemical constituents of these extracts (glucosides of quercetin and kaempferol), while vehicle OO showed the same effects, probably due to its constituent oleuropein.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Kainic Acid; Lipid Peroxides; Seizures; Tilia americana var. mexicana.
Copyright © 2022, Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Cardenas-Rodriguez N, Gonzalez-Trujano ME, Aguirre-Hernandez E, Ruiz-Garcia M, Sampieri A3, Coballase-Urrutia E, et al. Anticonvulsant and antioxidant effects of Tilia americana var. mexicana and flavonoids constituents in the pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:329172. doi: 10.1155/2014/329172. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carmona-Aparicio L, Ortega D, González-Trujano M, Rodríguez Chávez JL, Aguirre-Hernández E, Sampieri A, et al. Ethyl acetate extract of Tilia americana var. mexicana, a new cytotoxicity and antioxidant agent. J Food Agric Environ. 2014;12:78–81.
-
- Coballase-Urrutia E, Cardenas-Rodriguez N, Gonzalez-Garcia MC, Nunez-Ramirez E, Floriano-Sanchez E, Gonzalez-Trujano ME, et al. Biochemical and molecular modulation of CCl4-induced peripheral and central damage by Tilia americana var. mexicana extracts. Saudi Pharm J. 2017;25(3):319–31. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2016.06.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
