Some natural compounds and their analogues having potent anti- SARS-CoV-2 and anti-proteases activities as lead molecules in drug discovery for COVID-19
- PMID: 36060987
- PMCID: PMC9420082
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ejmcr.2022.100079
Some natural compounds and their analogues having potent anti- SARS-CoV-2 and anti-proteases activities as lead molecules in drug discovery for COVID-19
Abstract
Currently an emerging human pathogenic coronavirus, severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), caused coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that has posed a serious threat to public health worldwide. As it is a novel severe pneumonia-type viral disease, no effective therapeutic agents are available to treat this infection to date, emphasizing an urgent need for development of effective anti-SARS-CoV-2 agents. Based on screening in computational biology and biological in vitro assays, a good number of natural compounds and their synthetic analogues have been confirmed to possess target-specific inhibitory effects against the activity of host and viral proteases, namely, cathepsin-L, TMPRSS2, Sec61, Mpro (3CL-protease), RNA-dependent RNA protease (RdRp), helicase cap-binding proteases eEF1A, eIF4A, eIF4E, which play dominant roles in progression of infection and replication of SARS-CoV-2 virus in host cells. This review paper describes the potent antiviral activity and target-specific anti-proteases activity of some natural compounds and their synthetic analogues against SARS-CoV-2 infection. It will inspire the researchers to unleash their own creativity and to design potent and safe drugs to fight the current COVID-19 pandemic.
Keywords: COVID-19; COVID-19, coronavirus disease-2019; Host/virus proteases inhibitors; Natural analogues; Natural compounds; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

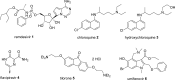
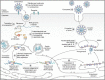

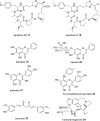
References
-
- Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic. http://www.who.int./emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/ad group... Available at: Accessed.
-
- Zhou P., Yang X.L., Wang X.G., Hu B., Zhang L., Zhang W., Shi H.R., Zhu Y., Li B., Huang C.L., Chen H.D., Chen J., Luo Y., Guo H., Jiang R.D., Liu M.Q., Chen Y., Shen X.R., Wang X., Zheng X.S., Zhao K., Chen Q.J., Deng F., Liu L.L., Yan B., Zhan R.X., Wang Y.Y., Xiao G.F., Shi Z.L. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature. 2020;579(7798):270–273. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
