Acute non-A, non-B, non-C hepatitis differences and similarities between hepatitis E virus infection and autoimmune hepatitis, with phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis E virus in humans and wild boars
- PMID: 36061156
- PMCID: PMC9399571
- DOI: 10.20524/aog.2022.0731
Acute non-A, non-B, non-C hepatitis differences and similarities between hepatitis E virus infection and autoimmune hepatitis, with phylogenetic analysis of hepatitis E virus in humans and wild boars
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis E virus (HEV) infection incidence is increasing in Europe, accounting for the majority of acute hepatitis cases. We investigated the prevalence and clinical characteristics of acute hepatitis E (AHE) in patients with acute non-A/B/C hepatitis from central Greece, their differences from acute autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) patients and the molecular similarity of human strains to local HEV strains in wild boars.
Methods: Sera from 20 patients with non-A/B/C acute hepatitis (2015-2017) were tested prospectively for anti-HEV IgM, IgG antibodies and HEV-RNA. Sera from patients diagnosed with acute AIH (2000-2015; n=56) were tested retrospectively. Liver tissue samples from 40 wild boars were tested for HEV-RNA. Positive wild boar and patients' samples were sequenced and phylogenetically analyzed.
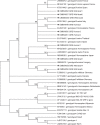
Results: Twelve of the 76 (16%) patients were diagnosed with AHE: HEV-RNA 11.5x104 (38.7-39.7x106) IU/mL; 11/20 (55%) acute non-A/B/C hepatitis and 1/56 (2%) AIH patients. Patients with AHE were older than those without, predominately men, with higher alanine aminotransferase but lower IgG levels (P=0.005 and P=0.002, respectively), and had high titers of smooth muscle antibodies. Liver biopsies, performed in 6/12 patients with HEV infection, revealed histology compatible with AIH. HEV strains from both patients and wild boars belonged to genotype 3.
Conclusions: Approximately one sixth of patients with acute non-A/B/C hepatitis had autochthonous HEV infection with AIH features. Therefore, a careful workup to exclude HEV should be carried out in all acute hepatitis cases before a definite diagnosis of AIH is established. Wild boars seem to be an important reservoir of HEV in Greece.
Keywords: Hepatitis E virus; acute autoimmune hepatitis; genotyping; wild boars.
Copyright: © Hellenic Society of Gastroenterology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: None
Figures
References
-
- WHO. Hepatitis E: fact sheet 2020. [Accessed 14 June 2022]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-e .
-
- Velavan TP, Pallerla SR, Johne R, et al. Hepatitis E: An update on one health and clinical medicine. Liver Int. 2021;41:1462–1473. - PubMed
-
- Adlhoch C, Avellon A, Baylis SA, et al. Hepatitis E virus: Assessment of the epidemiological situation in humans in Europe, 2014/15. J Clin Virol. 2016;82:9–16. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
