Prediction of balance function for stroke based on EEG and fNIRS features during ankle dorsiflexion
- PMID: 36061607
- PMCID: PMC9433808
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2022.968928
Prediction of balance function for stroke based on EEG and fNIRS features during ankle dorsiflexion
Abstract
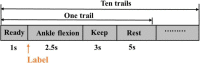
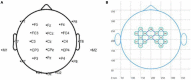
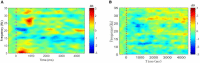
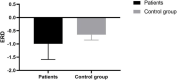
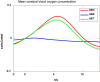
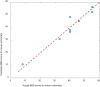
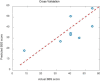
Balance rehabilitation is exceedingly crucial during stroke rehabilitation and is highly related to the stroke patients' secondary injuries (caused by falling). Stroke patients focus on walking ability rehabilitation during the early stage. Ankle dorsiflexion can activate the brain areas of stroke patients, similar to walking. The combination of electroencephalography (EEG) and functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) was a new method, providing more beneficial information. We extracted the event-related desynchronization (ERD), oxygenated hemoglobin (HBO), and Phase Synchronization Index (PSI) features during ankle dorsiflexion from EEG and fNIRS. Moreover, we established a linear regression model to predict Berg Balance Scale (BBS) values and used an eightfold cross validation to test the model. The results showed that ERD, HBO, PSI, and age were critical biomarkers in predicting BBS. ERD and HBO during ankle dorsiflexion and age were promising biomarkers for stroke motor recovery.
Keywords: EEG; balance rehabilitation; brain-computer interface; fNIRS; stroke.
Copyright © 2022 Liang, Song, Belkacem, Li, Liu, Chen, Wang, Wang and Wan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Current implications of EEG and fNIRS as functional neuroimaging techniques for motor recovery after stroke.Med Rev (2021). 2024 May 24;4(6):492-509. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0010. eCollection 2024 Dec. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39664080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Simultaneous EEG-fNIRS reveals how age and feedback affect motor imagery signatures.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Jan;49:183-197. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.10.011. Epub 2016 Oct 15. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 27818001
-
Bimodal Data Fusion of Simultaneous Measurements of EEG and fNIRS during Lower Limb Movements.Brain Sci. 2021 May 27;11(6):713. doi: 10.3390/brainsci11060713. Brain Sci. 2021. PMID: 34071982 Free PMC article.
-
Cortical changes underlying balance recovery in patients with hemiplegic stroke.Neuroimage. 2014 Jan 15;85 Pt 1:547-54. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2013.05.014. Epub 2013 May 16. Neuroimage. 2014. PMID: 23684871
-
Current State and Future Prospects of EEG and fNIRS in Robot-Assisted Gait Rehabilitation: A Brief Review.Front Hum Neurosci. 2019 Jun 5;13:172. doi: 10.3389/fnhum.2019.00172. eCollection 2019. Front Hum Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31231200 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of different types of RAGT on balance function in stroke patients with low levels of independent walking in a convalescent rehabilitation hospital.Open Med (Wars). 2025 Jun 27;20(1):20251212. doi: 10.1515/med-2025-1212. eCollection 2025. Open Med (Wars). 2025. PMID: 40585913 Free PMC article.
-
Strategic Integration: A Cross-Disciplinary Review of the fNIRS-EEG Dual-Modality Imaging System for Delivering Multimodal Neuroimaging to Applications.Brain Sci. 2024 Oct 16;14(10):1022. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14101022. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39452034 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current implications of EEG and fNIRS as functional neuroimaging techniques for motor recovery after stroke.Med Rev (2021). 2024 May 24;4(6):492-509. doi: 10.1515/mr-2024-0010. eCollection 2024 Dec. Med Rev (2021). 2024. PMID: 39664080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Early screening of post-stroke fall risk: A simultaneous multimodal fNIRs-EMG study.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Sep;30(9):e70041. doi: 10.1111/cns.70041. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39315509 Free PMC article.
-
A bibliometric analysis of electroencephalogram research in stroke: current trends and future directions.Front Neurol. 2025 Apr 28;16:1539736. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2025.1539736. eCollection 2025. Front Neurol. 2025. PMID: 40356632 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Basteris A., Nijenhuis S. M., Stienen A. H. A., Buurke J. H., Prange G. B., Amirabdollahian F., et al. (2014). Training modalities in robot-mediated upper limb rehabilitation in stroke: A framework for classification based on a systematic review. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 11:111. 10.1186/1743-0003-11-111 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Buchbinder B. R. (2016). Functional magnetic resonance imaging. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 135 61–92. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

