Electroacupuncture of Baihui and Shenting ameliorates cognitive deficits via Pten/Akt pathway in a rat cerebral ischemia injury model
- PMID: 36062010
- PMCID: PMC9437581
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2022.855362
Electroacupuncture of Baihui and Shenting ameliorates cognitive deficits via Pten/Akt pathway in a rat cerebral ischemia injury model
Abstract
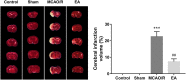
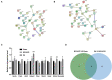
Cerebral ischemic stroke is a huge threat to the health and life of many people. Electroacupuncture (EA) at Baihui (GV20) and Shenting (GV24) acupoints can notably alleviate cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury (CIRI). However, the molecular basis underlying the effectiveness of EA at the GV20 and GV24 acupoints for CIRI remains largely unknown. Our present study demonstrated that EA treatment at the GV20 and GV24 acupoints markedly alleviated middle cerebral artery occlusion/reperfusion (MCAO/R)-induced cognitive deficits and cerebral infarction in rats. Proteomics analysis revealed that 195 and 218 proteins were dysregulated in rat hippocampal tissues in the MCAO/R vs. sham group and thhhe EA vs. MCAO/R group, respectively. Moreover, 62 proteins with converse alteration trends in MCAO/R vs. sham and EA vs. MCAO/R groups were identified. These proteins might be implicated in the EA-mediated protective effect against MCAO/R-induced cerebral injury. GO enrichment analysis showed that 39 dysregulated proteins in the MCAO/R vs. sham group and 40 dysregulated proteins in the EA vs. MCAO/R group were related to brain and nerve development. Protein-protein interaction analysis of the abovementioned dysregulated proteins associated with brain and nerve development suggested that Pten/Akt pathway-related proteins might play major roles in regulating EA-mediated protective effects against MCAO/R-induced brain and nerve injury. Western blot assays demonstrated that Pak4, Akt3, and Efnb2 were expressed at low levels in the MCAO/R group vs. the sham group but at high levels in the EA group vs. the MCAO/R group. In conclusion, multiple proteins related to the protective effect of EA at the GV20 and GV24 acupoints against CIRI were identified in our study.
Keywords: Baihui; Shenting; acupuncture; cerebral ischemia stroke; proteomics.
Copyright © 2022 Su, Hao, Lv, Wu, Li, Hu, Zhang, Gao and Feng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




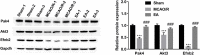
Similar articles
-
[Effects of electroacupuncture on mitochondrial autophagy and Sirt1/FOXO3/PINK1/Parkin pathway in rats with learning-memory impairment after cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury].Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025 Feb 12;45(2):193-9. doi: 10.13703/j.0255-2930.20231012-k0005. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu. 2025. PMID: 39943761 Chinese.
-
[Electroacupuncture ameliorates ischemic injury in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion rats by regulating endogenous melatonin and inhibiting the activation of astrocytes].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022 Jan 25;47(1):39-45. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20210738. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2022. PMID: 35128869 Chinese.
-
Electroacupuncture Ameliorates Neuronal Damage and Neurological Deficits after Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via Restoring Telomerase Reverse Transcriptase.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025 Mar;83(1):717-727. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01504-5. Epub 2024 Sep 5. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2025. PMID: 39235509
-
Electroacupuncture Regulates Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity via Inhibiting Janus-Activated Kinase 2/Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Signaling in Cerebral Ischemic Rats.J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019 Mar;28(3):792-799. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2018.11.025. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019. PMID: 30552029
-
Electroacupuncture alleviates neurological function via activating the Yap-OPA1 axis and mitochondrial fusion in rats with cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury.Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Nov 25;48(11):1088-1094. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20230345. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37984905 Chinese, English.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture improves spatial learning and memory impairment caused by herpes simplex virus type-1 in rats through the p38 MAPK/CREB pathway.J Physiol Sci. 2024 Oct 3;74(1):49. doi: 10.1186/s12576-024-00941-4. J Physiol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39363248 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of electroacupuncture at Baihui and Dazhui on perioperative neurocognitive impairment and S100-β, LC3-II, Beclin-1 in patients with colon cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Jun 15;15(6):4237-4245. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 37434809 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Role of Electroacupuncture Against Cognitive Impairment in Neurological Diseases.Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025;23(2):145-171. doi: 10.2174/1570159X22999240209102116. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2025. PMID: 38379403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics and its application in the research of acupuncture: An updated review.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 18;10(12):e33233. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33233. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39022010 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enhanced response and safety of combining dunhuang 'moxibustion classic' acupuncture with carbamazepine in treating neuropathic tinnitus and identifying risk factors affecting sleep quality.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Nov 15;16(11):6435-6446. doi: 10.62347/CQIR3328. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39678612 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

