Transplantation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuates Acute Liver Failure in Mice via an Interleukin-4-dependent Switch to the M2 Macrophage Anti-inflammatory Phenotype
- PMID: 36062289
- PMCID: PMC9396329
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00127
Transplantation of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuates Acute Liver Failure in Mice via an Interleukin-4-dependent Switch to the M2 Macrophage Anti-inflammatory Phenotype
Abstract
Background and aims: Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from bone marrow (BM) is an alternative treatment of acute liver failure (ALF) mainly because of the resulting anti-inflammatory activity. It is not known how MSCs regulate local immune responses and liver regeneration. This study explored the effects of MSCs on hepatic macrophages and the Wnt signaling pathway in ALF.
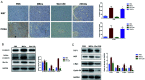
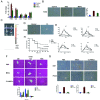
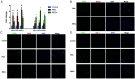
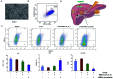
Methods: MSCs were isolated from BM aspirates of C57BL/6J mice, and transplanted in mice with ALF induced by D-galactosamine (D-Gal). The proliferation of hepatocytes was assayed by immunohistochemical (IHC) staining of Ki-67 and proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). The levels of key proteins in the Wnt signaling pathway were assayed by western blotting and cytokines were determined enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). A macrophage polarization assay characterized the M1/M2 ratio. The potential role of interleukin-4 (IL-4) in the biological activity of MSCs was determined by silencing of IL-4.
Results: Transplantation of allogeneic MSCs significantly attenuated D-Gal-induced hepatic inflammation and promoted liver regeneration. MSC transplantation significantly promoted a phenotypic switch from proinflamatory M1 macrophages to anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages, leading to significant Wnt-3a induction and activation of the Wnt signaling pathway in mice with D-Gal-induced ALF. Of the paracrine factors secreted by MSCs (G-CSF, IL-6, IL-1 beta, IL-4, and IL-17A), IL-4 was specifically induced following transplantation in the ALF model mice. The silencing of IL-4 significantly abrogated the phenotypic switch to M2 macrophages and the protective effects of MSCs in both the ALF model mice and a co-culture model in an IL-4 dependent manner.
Conclusions: In vivo and in vitro studies showed that MSCs ameliorated ALF through an IL-4-dependent macrophage switch toward the M2 anti-inflammatory phenotype. The findings may have clinical implications in that overexpression of IL-4 may enhance the therapeutic effects of allogeneic MSC transplantation in the treatment of ALF.
Keywords: Acute liver failure; Interleukin 4; Macrophage; Mesenchymal stem cells; Wnt signaling pathway.
© 2022 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate rhabdomyolysis-induced acute kidney injury via the activation of M2 macrophages.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Jun 24;5(3):80. doi: 10.1186/scrt469. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24961539 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-10 Contributes to Therapeutic Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Acute Liver Failure via Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 Signaling Pathway.Chin Med J (Engl). 2016 Apr 20;129(8):967-75. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.179794. Chin Med J (Engl). 2016. PMID: 27064043 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells rescue acute hepatic failure by polarizing M2 macrophages.World J Gastroenterol. 2017 Dec 7;23(45):7978-7988. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i45.7978. World J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 29259373 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue repair and regeneration.Biofactors. 2020 Mar;46(2):263-275. doi: 10.1002/biof.1587. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Biofactors. 2020. PMID: 31755595 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of acute liver failure.World J Gastroenterol. 2022 Jul 28;28(28):3627-3636. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v28.i28.3627. World J Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36161038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Applications of plant-derived extracellular vesicles in medicine.MedComm (2020). 2024 Sep 20;5(10):e741. doi: 10.1002/mco2.741. eCollection 2024 Oct. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 39309692 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioinspired Spatially Ordered Multicellular Lobules for Liver Regeneration.Research (Wash D C). 2025 Mar 17;8:0634. doi: 10.34133/research.0634. eCollection 2025. Research (Wash D C). 2025. PMID: 40099268 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate chronic liver damage via microRNA-136-5p.Mol Cell Biochem. 2025 Feb;480(2):951-969. doi: 10.1007/s11010-024-04993-3. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Mol Cell Biochem. 2025. PMID: 38652214
-
Immune-related gene SOX10 affects ferroptosis in pancreatic cancer and facilitates tumor progression by targeting CMTM7-mediated Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Eur J Med Res. 2025 Jan 4;30(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02177-9. Eur J Med Res. 2025. PMID: 39754171 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the Efficacy of Two Routes of Administration of Human Amniotic Epithelial Cells in Cell Therapy of Acute Hepatic Insufficiency.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 8;17(4):476. doi: 10.3390/ph17040476. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675436 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
