PSMB5 overexpression is correlated with tumor proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 36062301
- PMCID: PMC9623531
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13479
PSMB5 overexpression is correlated with tumor proliferation and poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
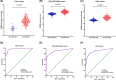
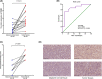
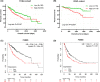
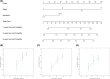
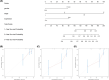
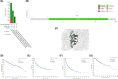
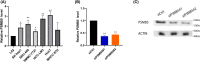
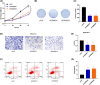
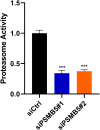
Aberrant expression of members of the proteasome subunit beta (PSMB) family (including PSMB2, PSMB4, PSMB7 and PSMB8) has been reported in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However the role of PSMB5 in HCC is unclear. To address this issue, we examined the expression of PSMB5 in HCC tissues using the The Cancer Genome Atlas, International Cancer Genome Consortium and Gene Expression Omnibus databases. A quantitative real-time PCR and immunohistochemistry were performed to validate the expression of PSMB5 in HCC. The survival mutation status and immune cell infiltration of PSMB5 were also evaluated in HCC. We then examined the effect of knocking down PSMB5 expression through RNA interference in the HCC cell line Huh7. High expression of PSMB5 was observed in HCC tissues and was associated with poor prognosis. PSMB5 expression and clinical characteristics were then incorporated to build a prognostic nomogram. We observed that PSMB5 expression was closely related to the abundance of B cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, dendritic cell macrophages and neutrophils. Moreover silencing of PSMB5 in Huh7 significantly suppressed cell proliferation and migration at the same time as increasing apoptosis. Inhibition of the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/mechanistic target of rapamycin pathway was observed after PSMB5 downregulation in Huh7 cells. Our findings suggest that PSMB5 may promote the proliferation of HCC cells by inactivating the phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt/mechanistic target of rapamycin signaling pathway and thus PSMB5 may have potential as a biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of HCC.
Keywords: PSMB5; diagnosis; prognosis; proliferation and hepatocellular carcinoma.
© 2022 The Authors. FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Llovet JM, Zucman‐Rossi J, Pikarsky E, Sangro B, Schwartz M, Sherman M, et al. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16018. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209–49. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J, Yu L, Gao X, Hu J, Wang J, Dai Z, et al. Plasma microRNA panel to diagnose hepatitis B virus‐related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29:4781–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

