Comparing the accuracy of the new-generation intraocular lens power calculation formulae in axial myopic eyes: a meta-analysis
- PMID: 36063246
- PMCID: PMC9971158
- DOI: 10.1007/s10792-022-02466-4
Comparing the accuracy of the new-generation intraocular lens power calculation formulae in axial myopic eyes: a meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: To compare the accuracy of the new-generation intraocular lens power calculation formulae in axial myopic eyes.
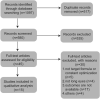
Methods: Four databases, PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE and Cochrane library, were searched to select relevant studies published between Apr 11, 2011, and Apr 11, 2021. Axial myopic eyes were defined as an axial length more than 24.5 mm. There are 13 formulae to participate in the final comparison (SRK/T, Hoffer Q, Holladay I, Holladay II, Haigis for traditional formulae, Barrett Universal II, Olsen, T2, VRF, EVO, Kane, Hill-RBF, LSF for the new-generation formulae). The primary outcomes were the percentage of eyes with a refractive prediction error in ± 0.5D and ± 1.0D.
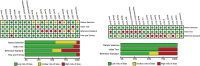
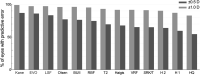
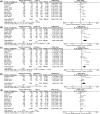
Results: A total of 2273 eyes in 15 studies were enrolled in the final meta-analysis. Overall, the new-generation formulae showed a relatively more accurate outcome in comparison with traditional formulae. The percentage of eyes with a predictive refraction error in ± 0.5D (± 1.0D) of Kane, EVO and LSF was higher than 80% (95%), which was only significantly different from Hoffer Q (all P < 0.05). Moreover, another two new-generation formulae, Barrett Universal II and Olsen, had higher percentages than SRK/T, Hoffer Q, Holladay I and Haigis for eyes with predictive refraction error in ± 0.5D and ± 1.0D (all P < 0.05). In ± 0.5D group, Hill-RBF was better than SRK/T (P = 0.02), and Holladay I was better than EVO (P = 0.03) and LSF (P = 0.009), and Hoffer Q had a lower percentage than EVO, Kane, Hill-RBF and LSF (P = 0.007, 0.004, 0.002, 0.03, respectively). Barrett Universal II was better than T2 (P = 0.02), and Hill-RBF was better than SRK/T (P = 0.009). No significant difference was found in other pairwise comparison.
Conclusion: The new-generation formula is more accurate in intraocular lens power calculation for axial myopic eyes in comparison with the third- or fourth-generation formula.
Keywords: Axial myopic; Cataract; IOL power calculation; Meta-analysis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Comparing the accuracy of new intraocular lens power calculation formulae in short eyes after cataract surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Int Ophthalmol. 2022 Jun;42(6):1939-1956. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-02191-4. Epub 2022 Jan 26. Int Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35080690
-
Comparison of the accuracy of twenty intraocular lens power calculation formulas in long eyes.Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2025 May-Jun;14(3):100198. doi: 10.1016/j.apjo.2025.100198. Epub 2025 Apr 10. Asia Pac J Ophthalmol (Phila). 2025. PMID: 40221046
-
A comparative analysis of 12 intraocular lens power formulas.Int Ophthalmol. 2021 Dec;41(12):4137-4150. doi: 10.1007/s10792-021-01966-z. Epub 2021 Jul 27. Int Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34318369
-
Comparison of the accuracy of 11 intraocular lens power calculation formulas.Eur J Ophthalmol. 2021 Sep;31(5):2370-2376. doi: 10.1177/1120672120962030. Epub 2020 Oct 15. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 33054421
-
Accuracy of intraocular lens power calculation formulae in short eyes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022 Mar;70(3):740-748. doi: 10.4103/ijo.IJO_934_21. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2022. PMID: 35225507 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Comparison of Barrett TK Universal II and Barrett Universal II TCRP Formulas in Power Calculations for 3 Presbyopia-Correcting Intraocular Lenses.Clin Ophthalmol. 2024 May 25;18:1457-1465. doi: 10.2147/OPTH.S461195. eCollection 2024. Clin Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38818525 Free PMC article.
-
Intraocular lens power calculation formulas: a scientometric analysis.Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol. 2023 Dec 31;12(3):115-126. doi: 10.51329/mehdiophthal1477. eCollection 2023 Fall. Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 38476575 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Segmented Optical Axial Length on the Performance of New-Generation Intraocular Lens Power Calculation Formulas in Extremely Long Eyes.J Clin Med. 2023 Nov 7;12(22):6959. doi: 10.3390/jcm12226959. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38002573 Free PMC article.
-
Level of Agreement of Intraocular Lens Power Measurements Between a Swept-Source OCT Biometer and a Partial Coherence Interferometer.J Clin Med. 2025 Jun 2;14(11):3903. doi: 10.3390/jcm14113903. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40507667 Free PMC article.
-
How to choose the intraocular lens power calculation formulas in eyes with extremely long axial length? A systematic review and meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 22;19(1):e0296771. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296771. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38252627 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

