Dilatational and shear rheology of soluble and insoluble monolayers with a Langmuir trough
- PMID: 36063630
- PMCID: PMC10038177
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.08.051
Dilatational and shear rheology of soluble and insoluble monolayers with a Langmuir trough
Abstract
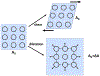
Hypothesis: The surface dilatational and shear moduli of surfactant and protein interfacial layers can be derived from surface pressures measured with a Wilhelmy plate parallel, ΔΠpar and perpendicular ΔΠperp to the barriers in a Langmuir trough.
Experimental: Applying area oscillations, A0+ ΔAeiωt, in a rectangular Langmuir trough induces changes in surface pressure, ΔΠpar and ΔΠperp for monolayers of soluble palmitoyl-lysophosphatidylcholine (LysoPC), insoluble dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), and the protein β-lactoglobulin to evaluate Es∗+Gs∗=A0ΔΠparΔA and Es∗-Gs∗=A0ΔΠperpΔA. Gs∗ was independently measured with a double-wall ring apparatus (DWR) and Es∗ by area oscillations of hemispherical bubbles in a capillary pressure microtensiometer (CPM) and the results were compared to the trough measurements.
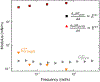
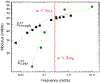
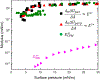
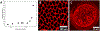
Findings: For LysoPC and DPPC, A0ΔΠparΔA≅A0ΔΠperpΔA meaning Es∗≫Gs∗ and Es∗≅A0ΔΠparΔA≅A0ΔΠperpΔA. Trough values for Es∗ were quantitatively similar to CPM when corrected for interfacial curvature. DWR showed G∗ was 4 orders of magnitude smaller than Es∗ for both LysoPC and DPPC. For β-lactoglobulin films, A0ΔΠparΔA>A0ΔΠperpΔA and Es∗ and Gs∗ were in qualitative agreement with independent CPM and DWR measurements. For β-lactoglobulin, both Es∗ and Gs∗ varied with film age and history on the trough, suggesting the evolution of the protein structure.
Keywords: DPPC; Dilatational modulus; Interfacial dilatational rheology; Interfacial rheology; Interfacial shear rheology; Lysolipids; Phospholipids; Soluble surfactant; β-lactoglobulin.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

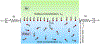
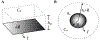
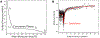
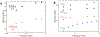
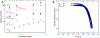
References
-
- Cicuta P, Terentjev EM, Viscoelasticity of a protein monolayer from anisotropic surface pressure measurements. Eur. Phys. J. E 16, 147–158 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Kanthe AD, Krause M, Zheng S, Ilott A, Bu W, Bera MK, Lin B, Maldarelli C, Tu RS, Armoring the interface with surfactants to prevent the adsorption of monoclonal antibodies. ACS Applied Mater Interfaces, (2020). - PubMed
-
- Alvarez NJ, Walker LM, Anna SL, Diffusion-limited adsorption to a spherical geometry: the impact of curvature and competitive time scales. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys 82, 011604 (2010). - PubMed
-
- Kotula AP, Anna SL, Insoluble layer deposition and dilatational rheology at a microscale spherical cap interface. Soft Matter 12, 7038–7055 (2016). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

