Detection of statin-induced rhabdomyolysis and muscular related adverse events through data mining technique
- PMID: 36064346
- PMCID: PMC9446837
- DOI: 10.1186/s12911-022-01978-4
Detection of statin-induced rhabdomyolysis and muscular related adverse events through data mining technique
Abstract
Background and objective: Rhabdomyolysis (RM) is a life-threatening adverse drug reaction in which statins are the one commonly related to RM. The study aimed to explore the association between statin used and RM or other muscular related adverse events. In addition, drug interaction with statins were also assessed.
Methods: All extracted prescriptions were grouped as lipophilic and hydrophilic statins. RM outcome was identified by electronically screening and later ascertaining by chart review. The study proposed 4 models, i.e., logistic regression (LR), Bayesian network (BN), random forests (RF), and extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost). Features were selected using multiple processes, i.e., bootstrapping, expert opinions, and univariate analysis.
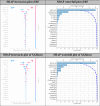
Results: A total of 939 patients who used statins were identified consisting 15, 9, and 19 per 10,000 persons for overall outcome prevalence, using statin alone, and co-administrations, respectively. Common statins were simvastatin, atorvastatin, and rosuvastatin. The proposed models had high sensitivity, i.e., 0.85, 0.90, 0.95 and 0.95 for LR, BN, RF, and XGBoost, respectively. The area under the receiver operating characteristic was significantly higher in LR than BN, i.e., 0.80 (0.79, 0.81) and 0.73 (0.72, 0.74), but a little lower than the RF [0.817 (95% CI 0.811, 0.824)] and XGBoost [0.819 (95% CI 0.812, 0.825)]. The LR model indicated that a combination of high-dose lipophilic statin, clarithromycin, and antifungals was 16.22 (1.78, 148.23) times higher odds of RM than taking high-dose lipophilic statin alone.
Conclusions: The study suggested that statin uses may have drug interactions with others including clarithromycin and antifungal drugs in inducing RM. A prospective evaluation of the model should be further assessed with well planned data monitoring. Applying LR in hospital system might be useful in warning drug interaction during prescribing.
Keywords: Bayesian network; Data mining; Drug interaction; Extreme gradient boosting; Random forests; Rhabdomyolysis; Statin.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Stahl K, Rastelli E, Schoser B. A systematic review on the definition of rhabdomyolysis. J Neurol. 2019. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

