MicroRNA-18a regulates the metastatic properties of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via HIF-1α expression
- PMID: 36064348
- PMCID: PMC9442921
- DOI: 10.1186/s12903-022-02425-6
MicroRNA-18a regulates the metastatic properties of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via HIF-1α expression
Abstract
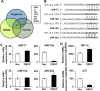
Background: Rapid metastasis of oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) is associated with a poor prognosis and a high mortality rate. However, the molecular mechanisms underlying OSCC metastasis have not been fully elucidated. Although deregulated expression of microRNA (miRNA) has a crucial role in malignant cancer progression, the biological function of miRNA in OSCC progression remains unclear. This study aimed to investigate the function of miRNA-18a in OSCC metastatic regulation via hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α).
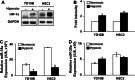
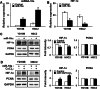
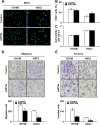
Methods: miRNA-18a-5p (miRNA-18a) expressions in patients with OSCC (n = 39) and in OSCC cell lines (e.g., YD-10B and HSC-2 cells) were analyzed using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. HIF-1α protein expressions in OSCC cells treated with miRNA-18a mimics or combined with cobalt chloride were analyzed using western blotting. The miRNA-18a expression-dependent proliferation and invasion abilities of OSCC cells were analyzed using MTT assay, EdU assay, and a Transwell® insert system.
Results: miRNA-18a expression was significantly lower in OSCC tissue than in the adjacent normal tissue. In OSCC cell lines, HIF-1α expression was significantly decreased by miRNA-18a mimic treatment. Furthermore, the migration and invasion abilities of OSCC cells were significantly decreased by miRNA-18a mimics and significantly increased by the overexpression of HIF-1α under hypoxic conditions relative to those abilities in cells treated only with miRNA-18a mimics.
Conclusions: miRNA-18a negatively affects HIF-1α expression and inhibits the metastasis of OSCC, thereby suggesting its potential as a therapeutic target for antimetastatic strategies in OSCC.
Keywords: HIF-1α; Hypoxia; Invasion; MicroRNA; Migration; Oral squamous cell carcinoma.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kuroshima T, Onozato Y, Oikawa Y, Ohsako T, Kugimoto T, Hirai H, Tomioka H, Michi Y, Miura M, Yoshimura R, et al. Prognostic impact of lingual lymph node metastasis in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue: a retrospective study. Sci Rep. 2021;11(1):20535. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-99925-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

