Differences in L-arginine metabolism and asthma morbidity among asthma patients with and without obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 36064404
- PMCID: PMC9442950
- DOI: 10.1186/s12931-022-02157-9
Differences in L-arginine metabolism and asthma morbidity among asthma patients with and without obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Background: Imbalance in L-arginine and nitric oxide (NO) metabolism has been implicated in the pathophysiology of asthma and obstructive sleep apnea (OSA), and both diseases impact the other's morbidity. We sought to determine whether L-arginine/NO metabolism differs between adults with asthma with or without comorbid OSA, and its association with asthma morbidity.
Methods: This is a cross-sectional study of 322 adults with asthma recruited in Denver, CO and New York City, NY. Data were collected on OSA status, spirometry, and metrics of asthma control and morbidity. L-Arginine metabolites were quantified in patient serum. Bivariate analyses and multiple regression were performed to determine differences between L-arginine metabolism, OSA and association with asthma morbidity.
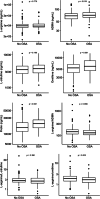
Results: Among the 322 participants, 92 (28.5%) had OSA. The cohort was 81.6% female, 23.4% identified as Black and 30.6% as Latino. Patients with asthma and OSA had significantly higher serum concentrations of NO synthase inhibitor asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) (p-value = 0.019), lower L-arginine to ornithine ratios (p-value = 0.003), and increased ornithine (p-value = 0.001) and proline levels (p-value < 0.001) compared to those without OSA. In adjusted models, OSA was associated with worse asthma control, adjusted mean difference in asthma control questionnaire of 0.36 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.06 to 0.65), and asthma quality of life questionnaire, adjusted mean difference: - 0.53 (95% CI: - 0.85 to - 0.21), after adjusting for relevant covariates including body mass index and L-arginine metabolites.
Conclusions: Adults with asthma and OSA had increased ADMA, an inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase, and greater metabolism of L-arginine via the arginase pathway compared to those with asthma alone, indicating a possible shared pathophysiological mechanism of these diseases.
Keywords: Asthma; Asthma epidemiology; Clinical epidemiology; Sleep apnea.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
MDA, GJ, RP, YJ, HG, ADF, and FH have no conflicts of interest to declare.
JPW- received consulting honorarium from Sanofi, Atea, Banook and PPD and research grants from Sanofi, Regeneron, and Arnold Consultants.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Phenotypic characteristics of asthma and morbidity are associated with distinct longitudinal changes in L-arginine metabolism.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023 Jun;10(1):e001683. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-001683. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37270184 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and CPAP Treatment on the Bioavailability of Erythrocyte and Plasma Nitric Oxide.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Nov 9;19(22):14719. doi: 10.3390/ijerph192214719. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36429438 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the relationship between comorbid obstructive sleep apnea and clinical outcomes in patients with asthma in Japan.Allergol Int. 2024 Jul;73(3):390-396. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2024.01.009. Epub 2024 Feb 9. Allergol Int. 2024. PMID: 38341371
-
Contribution of Obstructive Sleep Apnea to Asthmatic Airway Inflammation and Impact of Its Treatment on the Course of Asthma.Sleep Med Clin. 2024 Jun;19(2):261-274. doi: 10.1016/j.jsmc.2024.02.006. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Sleep Med Clin. 2024. PMID: 38692751 Review.
-
[Obstructive sleep apnea and asthma: Clinical implications].Rev Mal Respir. 2021 May;38(5):506-513. doi: 10.1016/j.rmr.2020.10.006. Epub 2021 May 18. Rev Mal Respir. 2021. PMID: 34020837 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Revisiting Asthma Obstructive Sleep Apnea Overlap: Current Knowledge and Future Needs.J Clin Med. 2023 Oct 16;12(20):6552. doi: 10.3390/jcm12206552. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37892689 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amino acid metabolism in health and disease.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 Sep 13;8(1):345. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01569-3. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37699892 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impact of Asthma and Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Central Airways Resistance During Pregnancy.Lung. 2025 Jun 3;203(1):66. doi: 10.1007/s00408-025-00817-3. Lung. 2025. PMID: 40459639
-
Phenotypic characteristics of asthma and morbidity are associated with distinct longitudinal changes in L-arginine metabolism.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023 Jun;10(1):e001683. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2023-001683. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2023. PMID: 37270184 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical