Resveratrol protection against IL-1β-induced chondrocyte damage via the SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling pathway
- PMID: 36064420
- PMCID: PMC9446849
- DOI: 10.1186/s13018-022-03306-y
Resveratrol protection against IL-1β-induced chondrocyte damage via the SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling pathway
Abstract
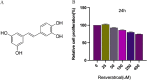
Purpose: Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common joint disease characterized by cartilage degeneration, synovial inflammation, osteophytes, and subchondral osteosclerosis. This study investigated the effects of resveratrol (RES) on extracellular matrix (ECM), autophagy, and apoptosis in OA pathogenesis via the SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway.
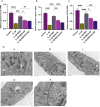
Methods: The microenvironment of OA chondrocytes was stimulated in vitro by adding 10 ng/mL of IL-1β to primary Wistar rat chondrocyte. Western blotting, immunofluorescence, quantitative real-time PCR, and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were used for analysis.
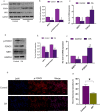
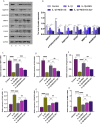
Results: In the presence of IL-1β, RES increased the expression of silent information regulator (SIR) 1 protein and the phosphorylation level of forkhead transcription factor (FOXO) 1. It also promoted chondrocyte autophagy, increased the expression of SOX9 and aggrecan, inhibited chondrocyte apoptosis and matrix breakdown, and protected chondrocytes from IL-1β damage. After a SIRT1 inhibitor or FOXO1 inhibitor was added, the protective effect of RES on chondrocytes was significantly weakened. Our results suggest that RES regulates the ECM metabolism, autophagy, and apoptosis of OA chondrocytes through the SIRT1/FOXO1 pathway to ameliorate IL-1β-induced chondrocyte injury.
Conclusion: RES protects chondrocytes from IL-1β-induced damage by activating SIRT1/FOXO1 signaling and holds potential in OA treatment.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Autophagy; Chondrocytes; Extracellular matrix; Osteoarthritis; Resveratrol.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Resveratrol Improves the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating the SIRT1-FoxO1 Pathway-Mediated Cholesterol Metabolism.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Jan 4;2023:2936236. doi: 10.1155/2023/2936236. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 36643587 Free PMC article.
-
Calycosin prevents IL-1β-induced articular chondrocyte damage in osteoarthritis through regulating the PI3K/AKT/FoxO1 pathway.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022 Jun;58(6):491-502. doi: 10.1007/s11626-022-00694-7. Epub 2022 Jun 15. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2022. PMID: 35705795
-
Circ_0022383 alleviates IL-1β-induced apoptosis, inflammation and extracellular matrix degeneration in osteoarthritis cell model by miR-3619-5p/SIRT1 axis.Int Immunopharmacol. 2022 Nov;112:109289. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.109289. Epub 2022 Oct 1. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36194985
-
The role of the sirtuin family in cartilage and osteoarthritis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 Dec 31;24(1):286. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02983-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36585687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role and current research status of resveratrol in the treatment of osteoarthritis and its mechanisms: a narrative review.Drug Metab Rev. 2024 Nov;56(4):399-412. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2024.2402751. Epub 2024 Oct 8. Drug Metab Rev. 2024. PMID: 39376171 Review.
Cited by
-
Resveratrol as sensitizer in colorectal cancer plasticity.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024 Mar;43(1):55-85. doi: 10.1007/s10555-023-10126-x. Epub 2023 Jul 29. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2024. PMID: 37507626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear binding SET domain 1 alleviates cartilage ferroptosis in knee osteoarthritis by upregulating the krüppel-like factor 9/autophagy-related 14 pathway via H3K36me2 modification.J Cell Commun Signal. 2025 Jun 29;19(3):e70027. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.70027. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Cell Commun Signal. 2025. PMID: 40584820 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of resveratrol on biochemical and structural outcomes in osteoarthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preclinical studies.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 4;10(13):e34064. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34064. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39055794 Free PMC article.
-
[Xinfeng Capsule alleviates interleukin-1β-induced chondrocyte inflammation and extracellular matrix degradation by regulating the miR-502-5p/TRAF2/NF-κB axis].Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024 Jan 20;44(1):108-118. doi: 10.12122/j.issn.1673-4254.2024.01.13. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 38293982 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Resveratrol Improves the Progression of Osteoarthritis by Regulating the SIRT1-FoxO1 Pathway-Mediated Cholesterol Metabolism.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Jan 4;2023:2936236. doi: 10.1155/2023/2936236. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 36643587 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ishidou Y, Matsuyama K, Sakuma D, Setoguchi T, Nagano S, Kawamura I, Maeda S, Komiya S. Osteoarthritis of the hip joint in elderly patients is most commonly atrophic, with low parameters of acetabular dysplasia and possible involvement of osteoporosis. Arch Osteoporos. 2017;12(1):30. doi: 10.1007/s11657-017-0325-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kang S, Kim JE, Song NR, Jung SK, Lee MH, Park JS, Yeom MH, Bode AM, Dong Z, Lee KW. The ginsenoside 20-O-beta-D-glucopyranosyl-20(S)-protopanaxadiol induces autophagy and apoptosis in human melanoma via AMPK/JNK phosphorylation. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(8):e104305. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104305. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

