Transplantation of human neural progenitor cells secreting GDNF into the spinal cord of patients with ALS: a phase 1/2a trial
- PMID: 36064599
- PMCID: PMC9499868
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01956-3
Transplantation of human neural progenitor cells secreting GDNF into the spinal cord of patients with ALS: a phase 1/2a trial
Abstract
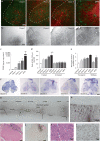
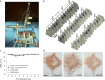
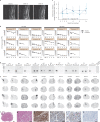
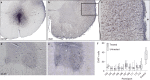
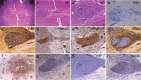
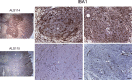
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) involves progressive motor neuron loss, leading to paralysis and death typically within 3-5 years of diagnosis. Dysfunctional astrocytes may contribute to disease and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF) can be protective. Here we show that human neural progenitor cells transduced with GDNF (CNS10-NPC-GDNF) differentiated to astrocytes protected spinal motor neurons and were safe in animal models. CNS10-NPC-GDNF were transplanted unilaterally into the lumbar spinal cord of 18 ALS participants in a phase 1/2a study (NCT02943850). The primary endpoint of safety at 1 year was met, with no negative effect of the transplant on motor function in the treated leg compared with the untreated leg. Tissue analysis of 13 participants who died of disease progression showed graft survival and GDNF production. Benign neuromas near delivery sites were common incidental findings at post-mortem. This study shows that one administration of engineered neural progenitors can provide new support cells and GDNF delivery to the ALS patient spinal cord for up to 42 months post-transplantation.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Cedars-Sinai owns the patent application related to the frame and cannula tested in this study. Pablo Avalos and Doniel Drazin are named on the patent application.
Figures
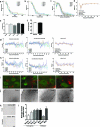
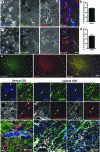



Comment in
-
A combined stem-cell-gene therapy strategy for ALS.Nat Med. 2022 Sep;28(9):1751-1752. doi: 10.1038/s41591-022-01983-0. Nat Med. 2022. PMID: 36097225 No abstract available.
-
Transplantation of neural progenitor cells into the human CNS.Trends Mol Med. 2022 Nov;28(11):897-899. doi: 10.1016/j.molmed.2022.09.009. Epub 2022 Sep 29. Trends Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 36182630
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

