The transferability of laparoscopic and open surgical skills to robotic surgery
- PMID: 36064750
- PMCID: PMC9446560
- DOI: 10.1186/s41077-022-00223-2
The transferability of laparoscopic and open surgical skills to robotic surgery
Abstract
Background: Within the last decades, robotic surgery has gained popularity. Most robotic surgeons have changed their main surgical activity from open or laparoscopic without prior formal robotic training. With the current practice, it is of great interest to know whether there is a transfer of surgical skills. In visualization, motion scaling, and freedom of motion, robotic surgery resembles open surgery far more than laparoscopic surgery. Therefore, our hypothesis is that open-trained surgeons have more transfer of surgical skills to robotic surgery, compared to surgeons trained in laparoscopy.
Methods: Thirty-six surgically inexperienced medical students were randomized into three groups for intensive simulation training in an assigned modality: open surgery, laparoscopy, or robot-assisted laparoscopy. The training period was, for all study subjects, followed by performing a robot-assisted bowel anastomosis in a pig model. As surrogate markers of surgical quality, the anastomoses were tested for resistance to pressure, and video recordings of the procedure were evaluated by two blinded expert robotic surgeons, using a global rating scale of robotic operative performance (Global Evaluative Assessment of Robotic Skills (GEARS)).
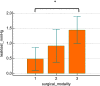
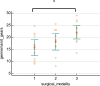
Results: The mean leak pressure of bowel anastomosis was 36.25 (7.62-64.89) mmHg in the laparoscopic training group and 69.01 (28.02-109.99) mmHg in the open surgery group, and the mean leak pressure for the robotic training group was 108.45 (74.96-141.94) mmHg. The same pattern was found with GEARS as surrogate markers of surgical quality. GEARS score was 15.71 (12.37-19.04) in the laparoscopic training group, 18.14 (14.70-21.58) in the open surgery group, and 22.04 (19.29-24.79) in the robotic training group. In comparison with the laparoscopic training group, the robotic training group had a statistically higher leak pressure (p = 0.0015) and GEARS score (p = 0.0023). No significant difference, for neither leak pressure nor GEARS, between the open and the robotic training group.
Conclusion: In our study, training in open surgery was superior to training in laparoscopy when transitioning to robotic surgery in a simulation setting performed by surgically naive study subjects.
Keywords: Assessment; Laparoscopy; Minimally invasive surgery; Open surgery; Robotics; Simulation training; Skill transfer; Surgical training.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Stolzenburg JU, Qazi HA, Holze S, Mende M, Nicolaus M, Franz T, et al. Evaluating the learning curve of experienced laparoscopic surgeons in robot-assisted radical prostatectomy. J Endourol. 2013;27(1):80–5. - PubMed
-
- Kim I.K. KJ, Park Y.A., et. al. Is prior laparoscopy experience required for adaptation to robotic rectal surgery?: feasibility of one-step transition from open to robotic surgery. Int J Colorectal Dis 2014:693-699. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

