Fuzi-Lizhong Decoction Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Blocking TLR4/MyD88/TRAF6 Signaling
- PMID: 36065267
- PMCID: PMC9440633
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1637701
Fuzi-Lizhong Decoction Alleviates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease by Blocking TLR4/MyD88/TRAF6 Signaling
Abstract
Background: Fuzi-Lizhong decoction (FLD) derives from the ancient Chinese Pharmacopoeia and has been clinically used for years. The present study aimed to investigate the activities and underlying mechanisms of FLD against nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
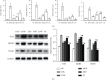
Methods: In vivo studies were conducted by inducing NAFLD in rats with a high-fat diet, and in vitro studies were performed on HL-7702 cells treated with oleic and linoleic acids. Total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), and blood glucose (Glu) levels were detected using an automatic biochemical analyzer. The expression of IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α in sera and cell culture supernatants was measured by ELISA. The mRNA and protein levels of TLR4, MyD88, and TRAF6 were measured in liver tissue and HL-7702 cells using reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction and western blot.
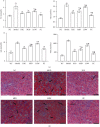
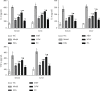
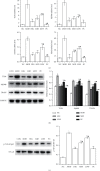
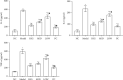
Results: FLD significantly reduced the TC, TG, Glu, FFA, IL-2, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in NAFLD rats and HL-7702 cells. Analysis of liver lipid content by Oil Red O staining revealed a significant increase in hepatic lipid accumulation in rats with NAFLD, but this lipid accumulation was reversed by FLD treatment. In addition, the mRNA expression levels of TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, and NF-κB p65 as well as the protein levels of TLR4, MyD88, TRAF6, and NF-κB p65 were decreased after FLD treatment. FLD significantly reduced inflammation and improved collagen accumulation in vivo and in vitro by inhibiting the activation of the TLR4/MyD88/TRAF6 signaling pathway.
Conclusions: FLD exerted potent protective effects against NAFLD via TLR4/MyD88/TRAF6 signaling. These findings provide novel insights into the mechanisms whereby this compound acts as an anti-inflammatory agent and highlight the potential application of FLD in the treatment of acute liver failure (ALF).
Copyright © 2022 Jiayao Yang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

