Advances in mass spectrometry imaging for spatial cancer metabolomics
- PMID: 36065601
- PMCID: PMC9986357
- DOI: 10.1002/mas.21804
Advances in mass spectrometry imaging for spatial cancer metabolomics
Abstract
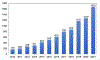
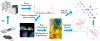
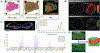
Mass spectrometry (MS) has become a central technique in cancer research. The ability to analyze various types of biomolecules in complex biological matrices makes it well suited for understanding biochemical alterations associated with disease progression. Different biological samples, including serum, urine, saliva, and tissues have been successfully analyzed using mass spectrometry. In particular, spatial metabolomics using MS imaging (MSI) allows the direct visualization of metabolite distributions in tissues, thus enabling in-depth understanding of cancer-associated biochemical changes within specific structures. In recent years, MSI studies have been increasingly used to uncover metabolic reprogramming associated with cancer development, enabling the discovery of key biomarkers with potential for cancer diagnostics. In this review, we aim to cover the basic principles of MSI experiments for the nonspecialists, including fundamentals, the sample preparation process, the evolution of the mass spectrometry techniques used, and data analysis strategies. We also review MSI advances associated with cancer research in the last 5 years, including spatial lipidomics and glycomics, the adoption of three-dimensional and multimodal imaging MSI approaches, and the implementation of artificial intelligence/machine learning in MSI-based cancer studies. The adoption of MSI in clinical research and for single-cell metabolomics is also discussed. Spatially resolved studies on other small molecule metabolites such as amino acids, polyamines, and nucleotides/nucleosides will not be discussed in the context.
Keywords: DESI; MALDI; SIMS; cancer; glycans; lipids; mass spectrometry imaging; spatial metabolomics.
© 2022 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
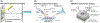
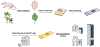

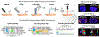
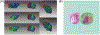
References
-
- Abbassi-Ghadi N, Jones EA, Veselkov KA, Huang J, Kumar S, Strittmatter N, Golf O, Kudo H, Goldin RD, Hanna GB, & Takats Z (2015). Repeatability and Reproducibility of Desorption Electrospray Ionization-Mass Spectrometry (DESI-MS) for the Imaging Analysis of Human Cancer Tissue: A Gateway for Clinical Applications. Anal. Methods 7, 71–80.
-
- Abdelmoula WM, Regan MS, Lopez BGC, Randall EC, Lawler S, Mladek AC, Nowicki MO, Marin BM, Agar JN, Swanson KR, Kapur T, Sarkaria JN, Wells W, & Agar NYR (2019). Automatic 3D Nonlinear Registration of Mass Spectrometry Imaging and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Data. Anal. Chem 91, 6206–6216. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aichler M, & Walch A (2015). MALDI Imaging Mass Spectrometry: Current Frontiers and Perspectives in Pathology Research and Practice. Lab. Invest 95, 422–431. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

