Heart rate changes and myocardial sodium
- PMID: 36065860
- PMCID: PMC9446395
- DOI: 10.14814/phy2.15446
Heart rate changes and myocardial sodium
Abstract
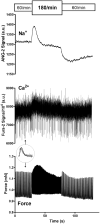
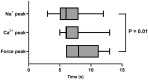
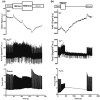
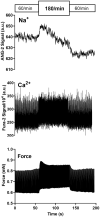
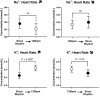
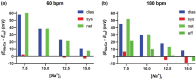
Historic studies with sodium ion (Na+ ) micropipettes and first-generation fluorescent probes suggested that an increase in heart rate results in higher intracellular Na+ -levels. Using a dual fluorescence indicator approach, we simultaneously assessed the dynamic changes in intracellular Na+ and calcium (Ca2+ ) with measures of force development in isolated excitable myocardial strip preparations from rat and human left ventricular myocardium at different stimulation rates and modeled the Na+ -effects on the sodium-calcium exchanger (NCX). To gain further insight into the effects of heart rate on intracellular Na+ -regulation and sodium/potassium ATPase (NKA) function, Na+ , and potassium ion (K+ ) levels were assessed in the coronary effluent (CE) of paced human subjects. Increasing the stimulation rate from 60/min to 180/min led to a transient Na+ -peak followed by a lower Na+ -level, whereas the return to 60/min had the opposite effect leading to a transient Na+ -trough followed by a higher Na+ -level. The presence of the Na+ -peak and trough suggests a delayed regulation of NKA activity in response to changes in heart rate. This was clinically confirmed in the pacing study where CE-K+ levels were raised above steady-state levels with rapid pacing and reduced after pacing cessation. Despite an initial Na+ peak that is due to a delayed increase in NKA activity, an increase in heart rate was associated with lower, and not higher, Na+ -levels in the myocardium. The dynamic changes in Na+ unveil the adaptive role of NKA to maintain Na+ and K+ -gradients that preserve membrane potential and cellular Ca2+ -hemostasis.
Keywords: calcium; heart rate; potassium; sodium.
© 2022 The Authors. Physiological Reports published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Physiological Society and the American Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest regarding this study.
Figures

References
-
- Bers, D. M. , & Bridge, J. H. (1989). Relaxation of rabbit ventricular muscle by Na‐Ca exchange and sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium pump. Ryanodine and voltage sensitivity. Circulation Research, 65, 334–342. - PubMed
-
- Bers, D. M. , & Weber, C. R. (2002). Na/Ca exchange function in intact ventricular myocytes. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 976, 500–512. - PubMed
-
- Blaustein, M. P. (1977). Sodium ions, calcium ions, blood pressure regulation, and hypertension: A reassessment and a hypothesis. The American Journal of Physiology, 232, C165–C173. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

