MET-Induced CD73 Restrains STING-Mediated Immunogenicity of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer
- PMID: 36066413
- PMCID: PMC9627131
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-22-0770
MET-Induced CD73 Restrains STING-Mediated Immunogenicity of EGFR-Mutant Lung Cancer
Abstract
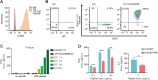
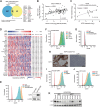
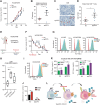
Immunotherapy has shown limited efficacy in patients with EGFR-mutated lung cancer. Efforts to enhance the immunogenicity of EGFR-mutated lung cancer have been unsuccessful to date. Here, we discover that MET amplification, the most common mechanism of resistance to third-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI), activates tumor cell STING, an emerging determinant of cancer immunogenicity (1). However, STING activation was restrained by ectonucleosidase CD73, which is induced in MET-amplified, EGFR-TKI-resistant cells. Systematic genomic analyses and cell line studies confirmed upregulation of CD73 in MET-amplified and MET-activated lung cancer contexts, which depends on coinduction of FOSL1. Pemetrexed (PEM), which is commonly used following EGFR-TKI treatment failure, was identified as an effective potentiator of STING-dependent TBK1-IRF3-STAT1 signaling in MET-amplified, EGFR-TKI-resistant cells. However, PEM treatment also induced adenosine production, which inhibited T-cell responsiveness. In an allogenic humanized mouse model, CD73 deletion enhanced immunogenicity of MET-amplified, EGFR-TKI-resistant cells, and PEM treatment promoted robust responses regardless of CD73 status. Using a physiologic antigen recognition model, inactivation of CD73 significantly increased antigen-specific CD8+ T-cell immunogenicity following PEM treatment. These data reveal that combined PEM and CD73 inhibition can co-opt tumor cell STING induction in TKI-resistant EGFR-mutated lung cancers and promote immunogenicity.
Significance: MET amplification upregulates CD73 to suppress tumor cell STING induction and T-cell responsiveness in TKI-resistant, EGFR-mutated lung cancer, identifying a strategy to enhance immunogenicity and improve treatment.
©2022 The Authors; Published by the American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures





References
-
- Soria JC, Ohe Y, Vansteenkiste J, Reungwetwattana T, Chewaskulyong B, Lee KH, et al. Osimertinib in untreated EGFR-mutated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 2018;378:113–25. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

