3-Chloro-5-Substituted-1,2,4-Thiadiazoles (TDZs) as Selective and Efficient Protein Thiol Modifiers
- PMID: 36066474
- PMCID: PMC9828193
- DOI: 10.1002/cbic.202200417
3-Chloro-5-Substituted-1,2,4-Thiadiazoles (TDZs) as Selective and Efficient Protein Thiol Modifiers
Abstract
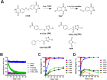
The study of cysteine modifications has gained much attention in recent years. This includes detailed investigations in the field of redox biology with focus on numerous redox derivatives like nitrosothiols, sulfenic acids, sulfinic acids and sulfonic acids resulting from increasing oxidation, S-lipidation, and perthiols. For these studies selective and rapid blocking of free protein thiols is required to prevent disulfide rearrangement. In our attempt to find new inhibitors of human histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) we discovered 5-sulfonyl and 5-sulfinyl substituted 1,2,4-thiadiazoles (TDZ), which surprisingly show an outstanding reactivity against thiols in aqueous solution. Encouraged by these observations we investigated the mechanism of action in detail and show that these compounds react more specifically and faster than commonly used N-ethyl maleimide, making them superior alternatives for efficient blocking of free thiols in proteins. We show that 5-sulfonyl-TDZ can be readily applied in commonly used biotin switch assays. Using the example of human HDAC8, we demonstrate that cysteine modification by a 5-sulfonyl-TDZ is easily measurable using quantitative HPLC/ESI-QTOF-MS/MS, and allows for the simultaneous measurement of the modification kinetics of seven solvent-accessible cysteines in HDAC8.
Keywords: biotin switch assay; covalent inactivators; nucleophilic aromatic substitution; proteomic studies; thiol modification.
© 2022 The Authors. ChemBioChem published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

