Renal effects of empagliflozin in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: from the EMPULSE trial
- PMID: 36066557
- PMCID: PMC9828037
- DOI: 10.1002/ejhf.2681
Renal effects of empagliflozin in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: from the EMPULSE trial
Abstract
Aim: The sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor empagliflozin improved clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure. In patients with chronic heart failure, SGLT2 inhibitors cause an early decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) followed by a slower eGFR decline over time than placebo. However, the effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on renal function during a hospital admission for acute heart failure remain largely unknown.
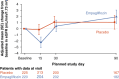
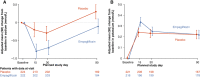
Methods and results: Between 1 and 5 days after a hospitalization for acute heart failure, 530 patients with an eGFR >20 ml/min/1.73 m2 were randomized to 10 mg of empagliflozin or placebo and treated for 90 days. Renal function and electrolytes were measured at baseline, and after 15, 30 and 90 days. We evaluated the effect of empagliflozin on eGFR over time and the impact of baseline eGFR on the primary hierarchical outcome of death, worsening heart failure events and quality of life. Mean baseline eGFR was 52.4 ml/min/1.73 m2 in the empagliflozin group and 55.7 ml/min/1.73 m2 in the placebo group. Empagliflozin caused an initial decline in eGFR (-2 ml/min/1.73 m2 at day 15 compared to placebo). At day 90, eGFR was similar between empagliflozin and placebo. Investigator-reported acute renal failure occurred in 7.7% of empagliflozin versus 12.1% of placebo patients. The overall clinical benefit (hierarchical composite of all-cause death, heart failure events and quality of life) of empagliflozin was unaffected by baseline eGFR.
Conclusion: In patients hospitalized for acute heart failure, empagliflozin caused an early modest decline in renal function which was no longer evident after 90 days. Acute renal events were similar in both groups. The clinical benefit of empagliflozin was consistent regardless of baseline renal function.
Keywords: Acute heart failure; Chronic kidney disease; Renal function; SGLT2 inhibitor.
© 2022 The Authors. European Journal of Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Figures

Comment in
-
Inhibiting the proximal nephron in acute heart failure - emerging data on kidney safety and efficacy.Eur J Heart Fail. 2022 Oct;24(10):1853-1855. doi: 10.1002/ejhf.2711. Eur J Heart Fail. 2022. PMID: 36193840 No abstract available.
References
-
- McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Køber L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al.; DAPA‐HF Trial Committees and Investigators . Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995–2008. - PubMed
-
- Packer M, Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Pocock SJ, Carson P, et al.; EMPEROR‐Reduced Trial Investigators . Cardiovascular and renal outcomes with empagliflozin in heart failure. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:1413–24. - PubMed
-
- Anker SD, Butler J, Filippatos G, Ferreira JP, Bocchi E, Böhm M, et al.; EMPEROR‐Preserved Trial Investigators . Empagliflozin in heart failure with a preserved ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:1451–61. - PubMed
-
- Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al.; EMPA‐REG OUTCOME Investigators . Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

