Discovery of Cyclic Peptide Inhibitors Targeting PD-L1 for Cancer Immunotherapy
- PMID: 36067356
- PMCID: PMC10671706
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00539
Discovery of Cyclic Peptide Inhibitors Targeting PD-L1 for Cancer Immunotherapy
Abstract
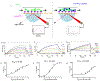
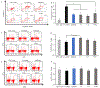
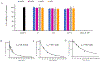
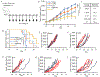
Blockade of the interaction between programmed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) and its receptor PD-1 has shown great success in cancer immunotherapy. Peptides possess unique characteristics that give them significant advantages as immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, unfavorable physicochemical properties and proteolytic stability profiles limit the translation of bioactive peptides as therapeutic agents. Studies have revealed that cyclization improves the biological activity and stability of linear peptides. In this study, we report the use of macrocyclization scanning for the discovery of cyclic anti-PD-L1 peptides with improved bioactivity. The cyclic peptides demonstrated up to a 34-fold improvement in the PD-1/PD-L1 blocking activity and significant in vivo anti-tumor activity. Our results demonstrate that macrocyclization scanning is an effective way to improve the serum stability and bioactivity of the anti-PD-L1 linear peptide. This strategy can be employed in the optimization of other bioactive peptides, particularly those for protein-protein interaction modulation.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests
We are in the process of filing a patent for the cyclic peptides discovered in this study.
Figures

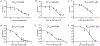
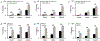
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Medical
Research Materials

