Mechanism and inhibition of BRAF kinase
- PMID: 36067564
- PMCID: PMC10396080
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2022.102205
Mechanism and inhibition of BRAF kinase
Abstract
The role of BRAF in tumor initiation has been established, however, the precise mechanism of autoinhibition has only been illustrated recently by several structural studies. These structures uncovered the basis by which the regulatory domains engage in regulating the activity of BRAF kinase domain, which lead to a more complete picture of the regulation cycle of RAF kinases. Small molecule BRAF inhibitors developed specifically to target BRAFV600E have proven effective at inhibiting the most dominant BRAF mutant in melanomas, but are less potent against other BRAF mutants in RAS-driven diseases due to paradoxical activation of the MAPK pathway. A variety of new generation inhibitors that do not show paradoxical activation have been developed. Alternatively, efforts have begun to develop inhibitors targeting the dimer interface of BRAF. A deeper understanding of BRAF regulation together with more diverse BRAF inhibitors will be beneficial for drug development in RAF or RASdriven cancers.
Keywords: 14-3-3; Allosteric kinase inhibitor; Autoinhibition; Paradoxical activation; RAF kinase; RAS; RAS-RAF interaction.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: Zhihong Wang reports financial support was provided by National Institute of Health. Zhihong Wang reports financial support was provided by WW Smith Charitable Foundation.
Figures
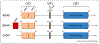
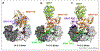
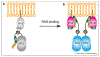

References
-
- Dorard C, Vucak G, Baccarini M: Deciphering the RAS/ERK pathway in vivo. Biochem Soc Trans 2017, 45:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Moodie SA, Willumsen BM, Weber MJ, Wolfman A: Complexes of Ras.GTP with Raf-1 and mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase. Science 1993, 260:1658–1661. - PubMed
-
- Freed E, Symons M, Macdonald SG, McCormick F, Ruggieri R: Binding of 14-3-3 proteins to the protein kinase Raf and effects on its activation. Science 1994, 265:1713–1716. - PubMed
-
- Dhillon AS, Yip YY, Grindlay GJ, Pakay JL, Dangers M, Hillmann M, Clark W, Pitt A, Mischak H, Kolch W: The C-terminus of Raf-1 acts as a 14-3-3-dependent activation switch. Cell Signal 2009, 21:1645–1651. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

