Extracellular sulfatase-2 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and mediates the TNF-α-induced inflammatory activation of synovial fibroblasts
- PMID: 36068294
- PMCID: PMC9508225
- DOI: 10.1038/s41423-022-00913-x
Extracellular sulfatase-2 is overexpressed in rheumatoid arthritis and mediates the TNF-α-induced inflammatory activation of synovial fibroblasts
Abstract
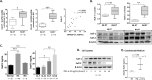
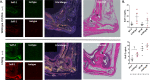
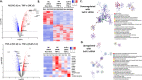
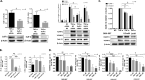
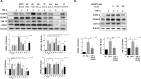
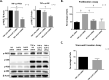
Extracellular sulfatase-2 (Sulf-2) influences receptor-ligand binding and subsequent signaling by chemokines and growth factors, yet Sulf-2 remains unexplored in inflammatory cytokine signaling in the context of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In the present study, we characterized Sulf-2 expression in RA and investigated its potential role in TNF-α-induced synovial inflammation using primary human RA synovial fibroblasts (RASFs). Sulf-2 expression was significantly higher in serum and synovial tissues from patients with RA and in synovium and serum from hTNFtg mice. RNA sequencing analysis of TNF-α-stimulated RASFs showed that Sulf-2 siRNA modulated ~2500 genes compared to scrambled siRNA. Ingenuity Pathway Analysis of RNA sequencing data identified Sulf-2 as a primary target in fibroblasts and macrophages in RA. Western blot, ELISA, and qRT‒PCR analyses confirmed that Sulf-2 knockdown reduced the TNF-α-induced expression of ICAM1, VCAM1, CAD11, PDPN, CCL5, CX3CL1, CXCL10, and CXCL11. Signaling studies identified the protein kinase C-delta (PKCδ) and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) pathways as key in the TNF-α-mediated induction of proteins related to cellular adhesion and invasion. Knockdown of Sulf-2 abrogated TNF-α-induced RASF proliferation. Sulf-2 knockdown with siRNA and inhibition by OKN-007 suppressed the TNF-α-induced phosphorylation of PKCδ and JNK, thereby suppressing the nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity of the transcription factors AP-1 and NF-κBp65 in human RASFs. Interestingly, Sulf-2 expression positively correlated with the expression of TNF receptor 1, and coimmunoprecipitation assays demonstrated the binding of these two proteins, suggesting they exhibit crosstalk in TNF-α signaling. This study identified a novel role of Sulf-2 in TNF-α signaling and the activation of RA synoviocytes, providing the rationale for evaluating the therapeutic targeting of Sulf-2 in preclinical models of RA.
Keywords: Rheumatoid arthritis; Signal transduction; Sulfatase-2; Synovial fibroblasts; TNF-α.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to CSI and USTC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Sulf2 mediates the effects of TNF in RASFs.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022 Nov;18(11):613. doi: 10.1038/s41584-022-00853-w. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2022. PMID: 36167820 No abstract available.
References
-
- Puimège L, Libert C, Van, Hauwermeiren F. Regulation and dysregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-1. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2014;25:285–300. - PubMed
-
- Locksley RM, Killeen N, Lenardo MJ. The TNF and TNF receptor superfamilies: integrating mammalian biology. Cell. 2001;104:487–501. - PubMed
-
- Lowenthal JW, Ballard DW, Bohnlein E, Greene WC. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces proteins that bind specifically to kappa B-like enhancer elements and regulate interleukin 2 receptor alpha-chain gene expression in primary human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1989;86:2331–5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Roach DR, Bean AG, Demangel C, France MP, Briscoe H, Britton WJ. TNF regulates chemokine induction essential for cell recruitment, granuloma formation, and clearance of mycobacterial infection. J Immunol. 2002;168:4620–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

