Safety and efficacy of double-balloon catheter for cervical ripening: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 36068489
- PMCID: PMC9450369
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-022-04988-2
Safety and efficacy of double-balloon catheter for cervical ripening: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Background: Various methods are used for cervical ripening during the induction of labor. Mechanical and pharmacological methods are commonly used for cervical ripening. A double-balloon catheter was specifically developed to ripen the cervix and induce labor; however, the efficacy of the double-balloon catheter in cervical ripening compared to other methods is unknown.
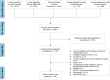
Methods: We searched five databases and performed a Bayesian network meta-analysis. Six interventions (double-balloon catheter, Foley catheter, oral misoprostol, vaginal misoprostol, dinoprostone, and double-balloon catheter combined with oral misoprostol) were included in the search. The primary outcomes were cesarean delivery rate and time from intervention-to-birth. The secondary outcomes were as follows: Bishop score increment; achieving a vaginal delivery within 24 h; uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate changes; need for oxytocin augmentation; instrumental delivery; meconium staining; chorioamnionitis; postpartum hemorrhage; low Apgar score; neonatal intensive care unit admission; and arterial pH.
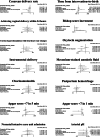
Results: Forty-eight randomized controlled trials involving 11,482 pregnant women were identified. The cesarean delivery rates of the cervical ripening with a double-balloon catheter and oral misoprostol, oral misoprostol, and vaginal misoprostol were significantly lower than cervical ripening with a Foley catheter (OR = 0.48, 95% CI: 0.23-0.96; OR = 0.74, 95% CI: 0.58-0.93; and OR = 0.79, 95% CI: 0.64-0.97, respectively; all P < 0.05). The time from intervention-to-birth of vaginal misoprostol was significantly shorter than the other five cervical ripening methods. Vaginal misoprostol and oral misoprostol increased the risk of uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate changes compared to a Foley catheter. A double-balloon catheter with or without oral misoprostol had similar outcomes, including uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate changes compared to a Foley catheter.
Conclusion: Double-balloon catheter did not show superiority when compared with other single method in primary and secondary outcomes of labor induction. The combination of double-balloon catheter with oral misoprostol was significantly reduced the rate of cesarean section compared to Foley catheter without increased risk of uterine hyperstimulation with fetal heart rate changes, which was shown in oral or vaginal misoprostol.
Keywords: Cervical ripening; Dinoprostone; Double-balloon catheter; Foley; Labor induction; Meta-analysis; Misoprostol.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Sciscione AC, McCullough H, Manley JS, Shlossman PA, Pollock M, Colmorgen GH. A prospective, randomized comparison of Foley catheter insertion versus intracervical prostaglandin E2 gel for preinduction cervical ripening. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999;180(1 Pt 1):55–60. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9378(99)70149-3. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Tenore JL. Methods for cervical ripening and induction of labor. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67(10):2123–2128. - PubMed
-
- ACOG Practice Bulletin No 107: Induction of labor. Obstet Gynecol. 2009;114(2 Pt 1):386–397. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

