Comparative study of a modified double-lumen tube ventilation control connector and traditional connector in clinical use: a randomised-controlled trial
- PMID: 36068501
- PMCID: PMC9446794
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-022-01816-0
Comparative study of a modified double-lumen tube ventilation control connector and traditional connector in clinical use: a randomised-controlled trial
Abstract
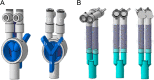
Background: A Y-shaped rotatable connector (YRC) for double-lumen tubes (DLT) is invented and compared with the traditional connector (Y-shaped connector, YC).
Methods: Sixty patients with ASA grade I-III, aged ≥ 18 years, who needed to insert a DLT for thoracic surgery were recruited and assigned into the YRC group (n = 30) and the YC group (n = 30) randomly. The primary endpoints included the inhaled air concentration (Fi) and the exhaled air concentration (Et) of sevoflurane before and after the switch between two-lung ventilation and one-lung ventilation at different times, positioning time, and switching time. The secondary endpoints were the internal gas volume of the two connectors, airway pressure, and the sputum suction time.
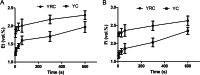
Results: The Et and Fi of the YRC group and the YC group were significantly different (all p < 0.05) at 5s, 10s, and 30s after the patient switched from two-lung ventilation to one-lung ventilation. The positioning time of the YRC group was less than YC group (89.75 ± 14.28 s vs 107.80 ± 14.96 s, p < 0.05), as well as the switching time (3.60 ± 1.20 s vs 9.05 ± 2.53 s, p < 0.05) and the internal gas volume (17.20 ml vs 24.12 ml). There was no difference in airway pressure and the sputum suction time in two groups.
Conclusion: Compared with YC, YRC was beneficial for maintaining depth of anesthesia, improves efficiency for the switch between one-lung and two-lung ventilation, and shortens the tube positioning time.
Keywords: Bronchial intubation; One-lung ventilation; Two-lung ventilation; double-lumen tube connector.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of left double lumen tube and y-shaped and double-ended bronchial blocker for one lung ventilation in thoracic surgery-a randomised controlled clinical trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2022 Apr 2;22(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s12871-022-01637-1. BMC Anesthesiol. 2022. PMID: 35366801 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of Arndt-endobronchial blocker plus laryngeal mask airway with left-sided double-lumen endobronchial tube in one-lung ventilation in thoracic surgery in the morbidly obese.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017 Dec 18;51(2):e6825. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20176825. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2017. Retraction in: Braz J Med Biol Res. 2018 Aug 16;51(10):e6825retraction. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X20176825retraction. PMID: 29267506 Free PMC article. Retracted. Clinical Trial.
-
[A comparison of double-lumen endotracheal tube with univent blocker and bronchial blocker during thoracic surgical anesthesia].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012 Sep 18;92(35):2481-4. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2012. PMID: 23158714 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Current Practice Issues in Thoracic Anesthesia.Anesth Analg. 2021 Dec 1;133(6):1520-1531. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0000000000005707. Anesth Analg. 2021. PMID: 34784334
-
[Airway Management in Thoracic Anesthesia with Double-Lumen Tube].Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2018 Mar;53(3):174-185. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-114678. Epub 2018 Mar 19. Anasthesiol Intensivmed Notfallmed Schmerzther. 2018. PMID: 29554710 Review. German.
References
-
- Cohen E. Recommendations for airway control and difficult airway management in thoracic anesthesia and lung separation procedures. Are we ready for the challenge? Minerva Anestesiol. 2009;75:3–5. - PubMed
-
- Roberts JD. Anesthesia for lung transplantation. Cardiac Anesthesia: A Problem Based Learning Approach. 2019. p. 322.
-
- Jung DM, Ahn HJ, Jung S-H, Yang M, Kim JA, Shin SM, Jeon S. Apneic oxygen insufflation decreases the incidence of hypoxemia during one-lung ventilation in open and thoracoscopic pulmonary lobectomy: a randomized controlled trial. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154(1):360–366. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2017.02.054. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

