Biofilm-Associated Multi-Drug Resistance in Hospital-Acquired Infections: A Review
- PMID: 36068834
- PMCID: PMC9441148
- DOI: 10.2147/IDR.S379502
Biofilm-Associated Multi-Drug Resistance in Hospital-Acquired Infections: A Review
Abstract
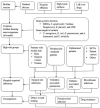
Biofilm-related multi-drug resistance (MDR) is a major problem in hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) that increase patient morbidity and mortality rates and economic burdens such as high healthcare costs and prolonged hospital stay. This review focuses on the burden of bacterial biofilm in the hospital settings, their impact on the emergence of MDR in the HAIs, biofilm detection methods, recent approaches against biofilms, and future perspectives. The prevalence of biofilm-associated MDR among HAIs ranges from 17.9% to 100.0% worldwide. The predominant bacterial isolates causing HAIs in recently published studies were S. aureus, A. baumannii, K. pneumoniae, and P. aeruginosa. In addition to the use of qualitative and quantitative methods to detect biofilm formation, advanced PCR-based techniques have been performed for detecting biofilm-associated genes. Although there are suggested therapeutic strategies against biofilms, further confirmation of their efficacy for in vivo application and antibiotics targeting biofilm-associated genes/proteins to minimize treatment failure is required for the future.
Keywords: biofilm; hospital-acquired infections; multi-drug resistance.
© 2022 Assefa and Amare.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
-
- Elhabibi T, Ramzy S. Biofilm production by multi drug resistant bacterial pathogens isolated from patients in intensive care units in Egyptian hospitals. J Microb Biochem Technol. 2017;9(4):151–158.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources