Dynamic FDG-PET demonstration of functional brain abnormalities
- PMID: 36069052
- PMCID: PMC9463948
- DOI: 10.1002/acn3.51546
Dynamic FDG-PET demonstration of functional brain abnormalities
Abstract
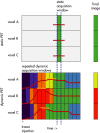
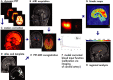
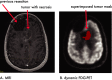
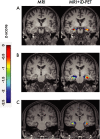
Positron emission tomography with fluorine-18 fluorodeoxyglucose (18 F-FDG-PET) has been used over 3 decades to map patterns of brain glucose metabolism to evaluate normal brain function or demonstrate abnormalities of metabolism in brain disorders. Traditional PET maps patterns of absolute tracer uptake but has demonstrated shortcomings in disorders such as brain neoplasm or focal epilepsy in the ability to resolve normally from pathological tissue. In this review, we describe an alternative process of metabolic mapping, dynamic PET. This new technology quantifies the dynamics of tracer uptake and decays with the goal of improving the functional mapping of the desired metabolic activity in the target organ. We discuss technical implementation and findings of initial pilot studies in brain tumor treatment and epilepsy surgery.
© 2022 The Authors. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Neurological Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kosaka N, Tsuchida T, Uematsu H, Kimura H, Okazawa H, Itoh H. 18F‐FDG PET of common enhancing malignant brain tumors. Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(6):W365‐W369. - PubMed
-
- Purandare NC, Puranik A, Shah S, et al. Common malignant brain tumors: can 18F‐FDG PET/CT aid in differentiation? Nucl Med Commun. 2017;38(12):1109‐1116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

