The role of IL-23 and the use of IL-23 inhibitors in psoriatic arthritis
- PMID: 36069174
- PMCID: PMC9825973
- DOI: 10.1002/msc.1694
The role of IL-23 and the use of IL-23 inhibitors in psoriatic arthritis
Abstract
Background: Psoriatic arthritis (PsA) is a chronic inflammatory arthritis characterised by musculoskeletal and extra-articular manifestations, most notably psoriasis. While the underlying pathogenetic mechanisms are not yet fully understood, a central role has been identified for the IL-23/IL-17 pathway.
Objectives: We briefly describe the role of IL-23 in the pathogenesis of PsA and go on to describe the available anti-IL-23 agents and their place in the management of PsA.
Methods: This is a narrative review of the current literature, focussing on the results of the phase 3 studies in PsA for the IL-12/23 p40 inhibitor ustekinumab and the more recent IL-23 p19 inhibitors guselkumab, risankizumab and tildrakizumab.
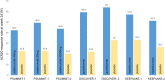
Results: IL-23 triggers expression of IL-17 and other effector cytokines in a variety of cells, leading to tissue inflammation and injury. Targeting IL-23, particularly with p19 inhibitors, appears to be an effective and safe strategy for multiple clinical domains in PsA, most notably the skin, with some differences in efficacy emerging between these agents.
Conclusion: The development of IL-23 inhibitors represents a significant advance in the management of psoriatic disease. In the absence of head-to-head studies, future data emerging from real-world experiences of individual IL-23 p19 inhibitors will help inform the use of these agents in relation to other biologics in PsA.
Keywords: guselkumab; interleukin-23; psoriatic arthritis; risankizumab; tildrakizumab; ustekinumab.
© 2022 The Authors. Musculoskeletal Care published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
George E Fragoulis declares: honoraria from: Abbvie, UCB,Janssen, Novartis, PFizer, Genesis, Lilly, Aenorasis. Stefan Siebert declares research funding from Amgen (previously Celgene), Boehringer‐Ingelheim, Bristol‐Myers Squibb, Eli Lilly, Janssen, and UCB and speaker/consultancy fees from AbbVie, Eli Lilly, GSK, Janssen, and UCB.
Figures

References
-
- Appel, H. , Maier, R. , Bleil, J. , Hempfing, A. , Loddenkemper, C. , Schlichting, U. , Syrbe, U. , & Sieper, J. (2013). In situ analysis of interleukin‐23‐ and interleukin‐12‐positive cells in the spine of patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis & Rheumatism, 65(6), 1522–1529. 10.1002/art.37937 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Araujo, E. G. , Englbrecht, M. , Hoepken, S. , Finzel, S. , Kampylafka, E. , Kleyer, A. , Bayat, S. , Schoenau, V. , Hueber, A. , Rech, J. , & Schett, G. (2019). Effects of ustekinumab versus tumor necrosis factor inhibition on enthesitis: Results from the enthesial clearance in psoriatic arthritis (ECLIPSA) study. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism, 48(4), 632–637. 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.05.011 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Baeten, D. , Ostergaard, M. , Wei, J. C. , Sieper, J. , Jarvinen, P. , Tam, L. S. , Salvarani, C. , Kim, T. H. , Solinger, A. , Datsenko, Y. , Pamulapati, C. , Visvanathan, S. , Hall, D. B. , Aslanyan, S. , Scholl, P. , & Padula, S. J. (2018). Risankizumab, an IL‐23 inhibitor, for ankylosing spondylitis: Results of a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, proof‐of‐concept, dose‐finding phase 2 study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 77(9), 1295–1302. 10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213328 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Belasco, J. , Louie, J. S. , Gulati, N. , Wei, N. , Nograles, K. , Fuentes‐Duculan, J. , Mitsui, H. , Suarez‐Farinas, M. , & Krueger, J. G. (2015). Comparative genomic profiling of synovium versus skin lesions in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis & Rheumatology, 67(4), 934–944. 10.1002/art.38995 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

